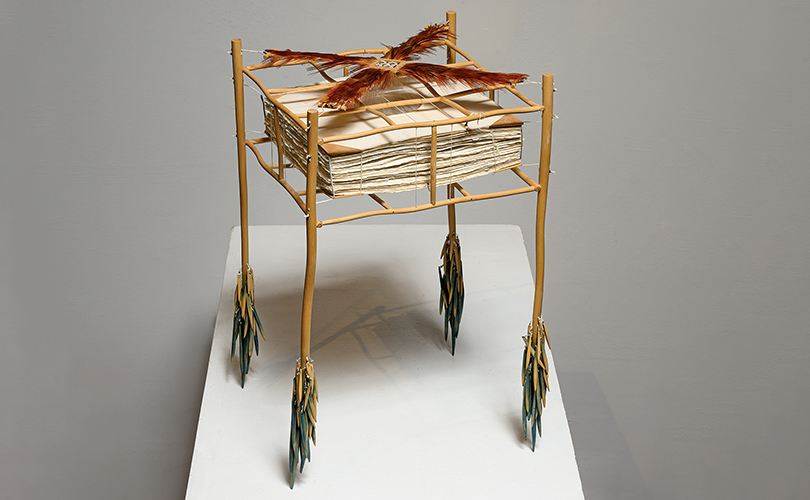
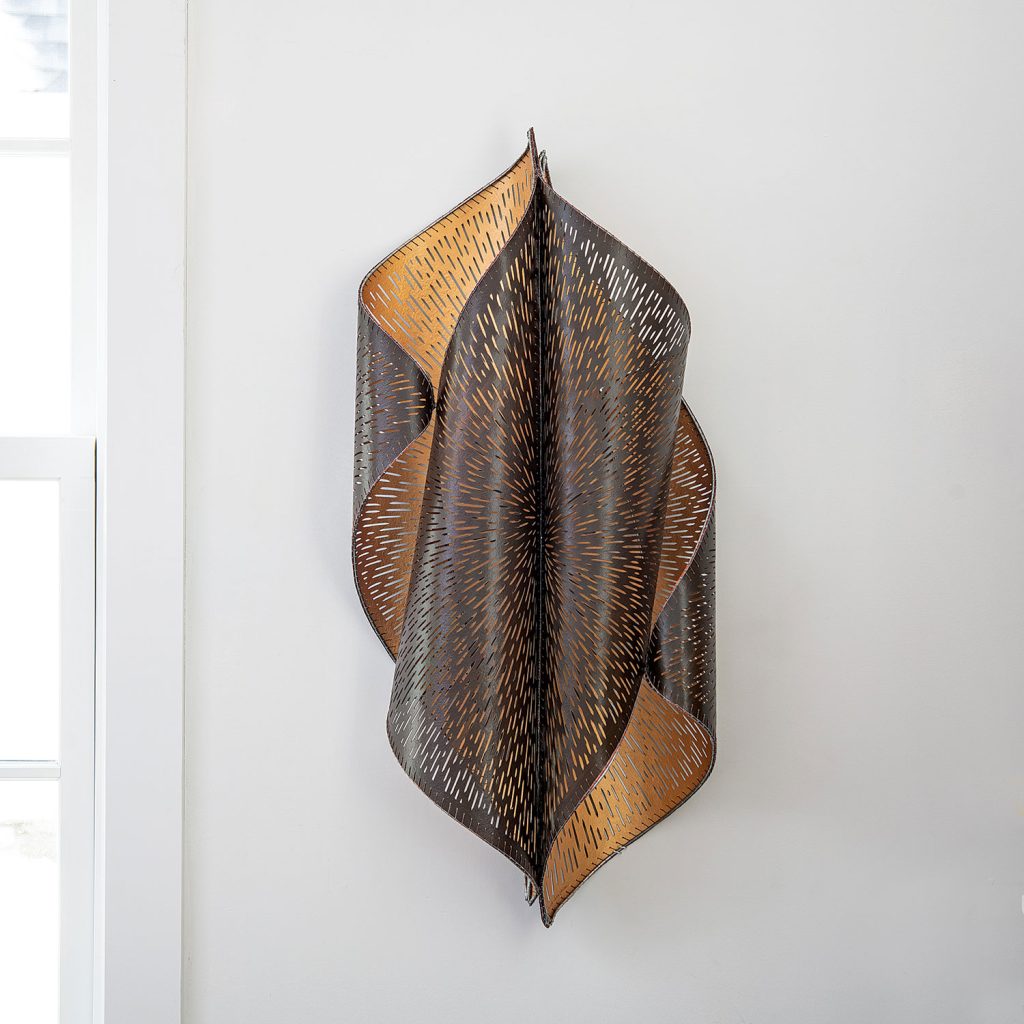
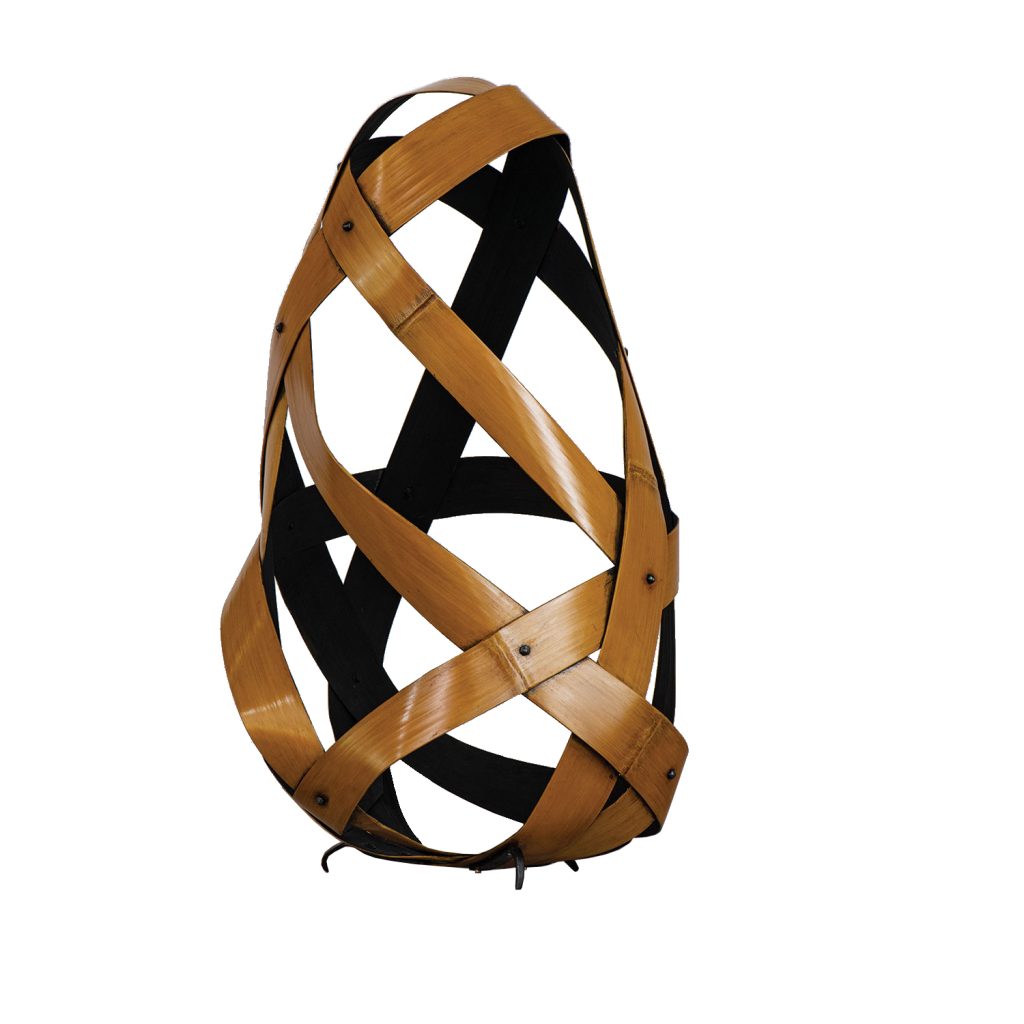
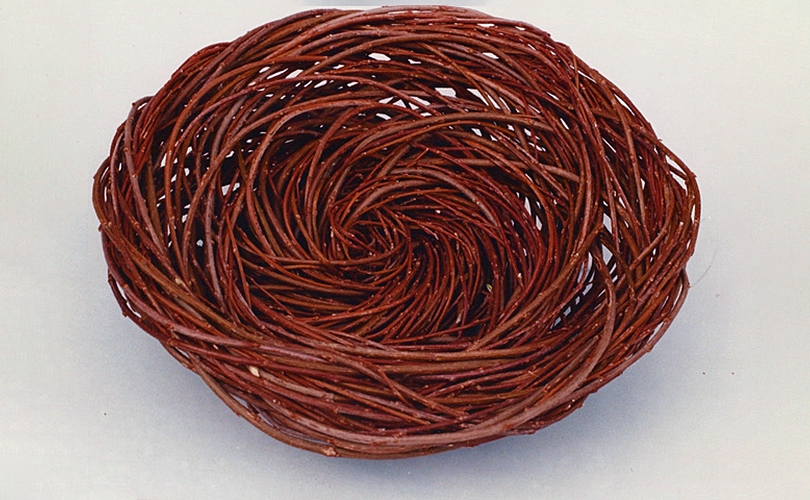
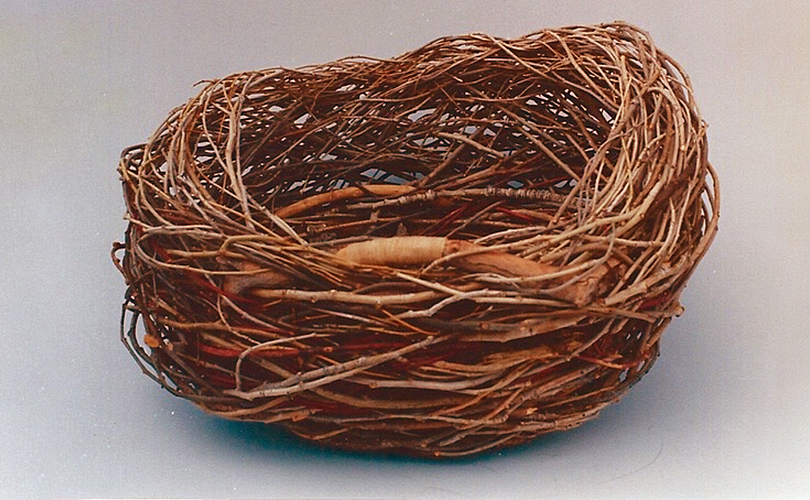
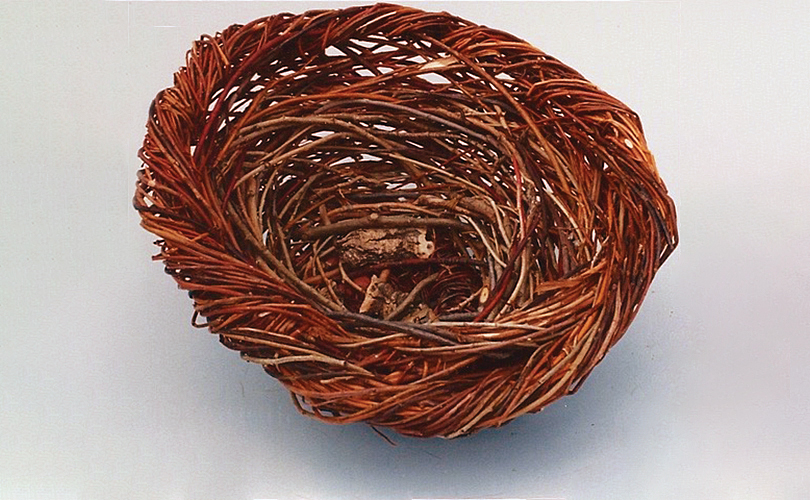
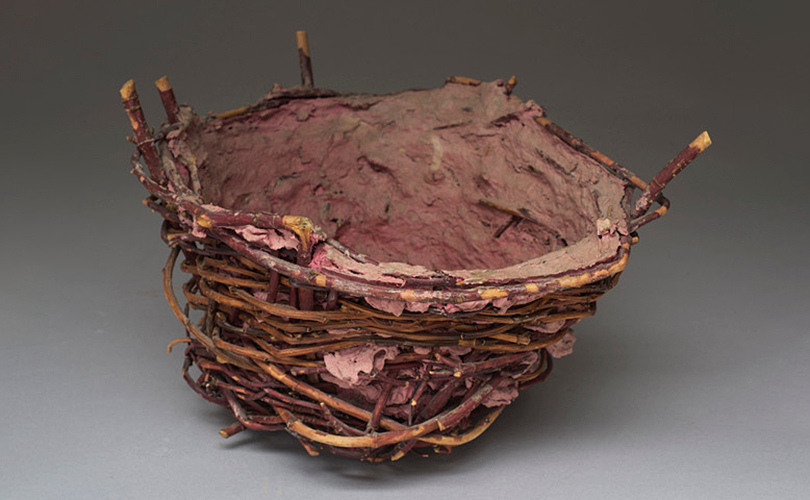
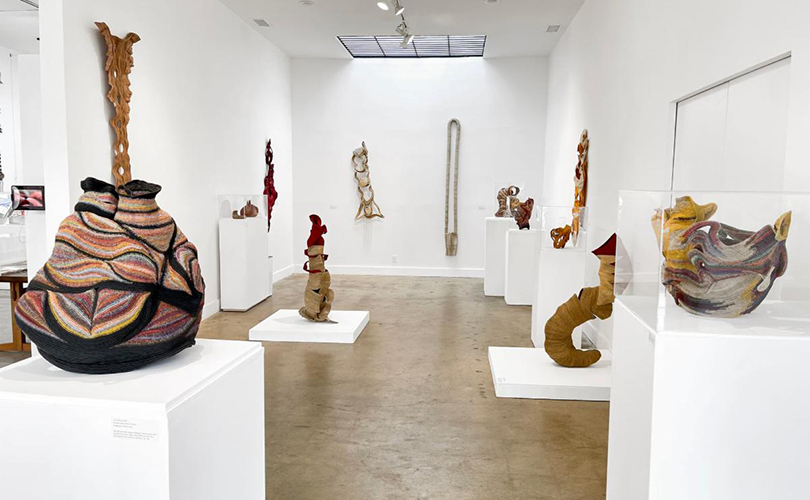
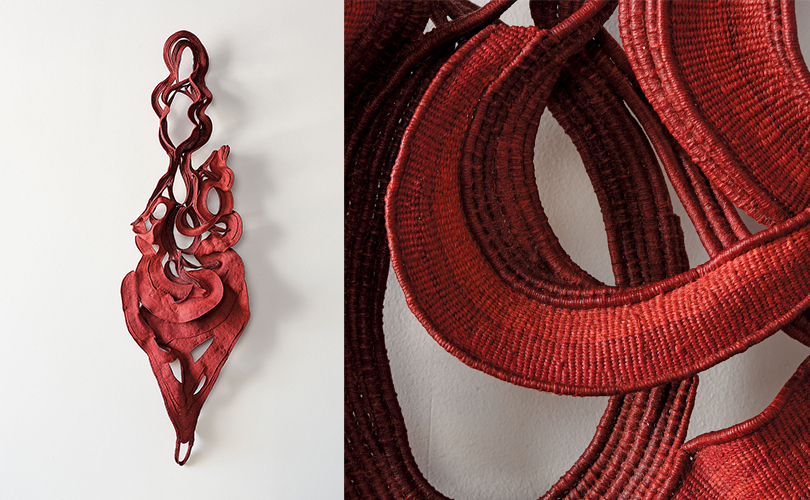
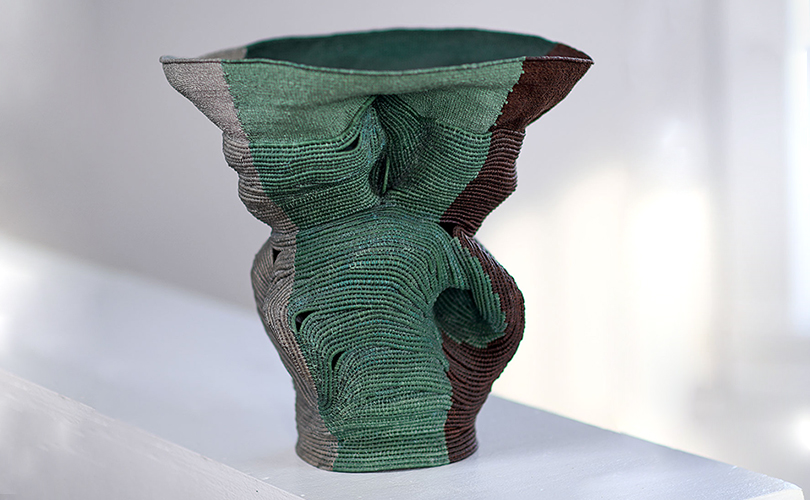
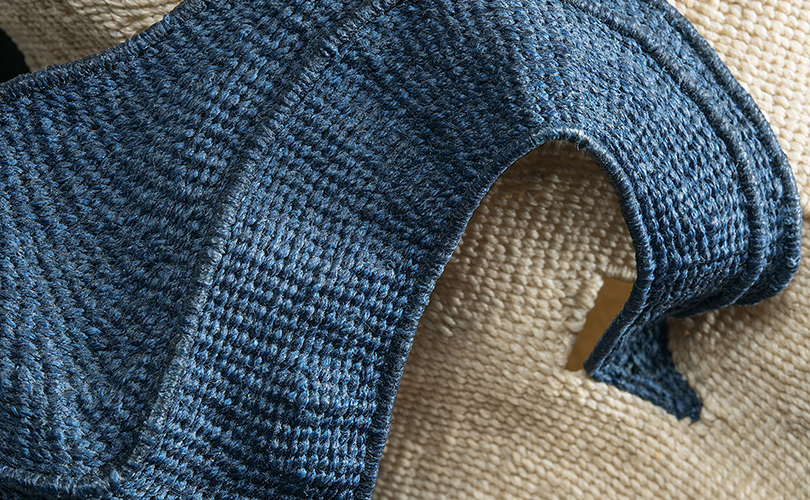
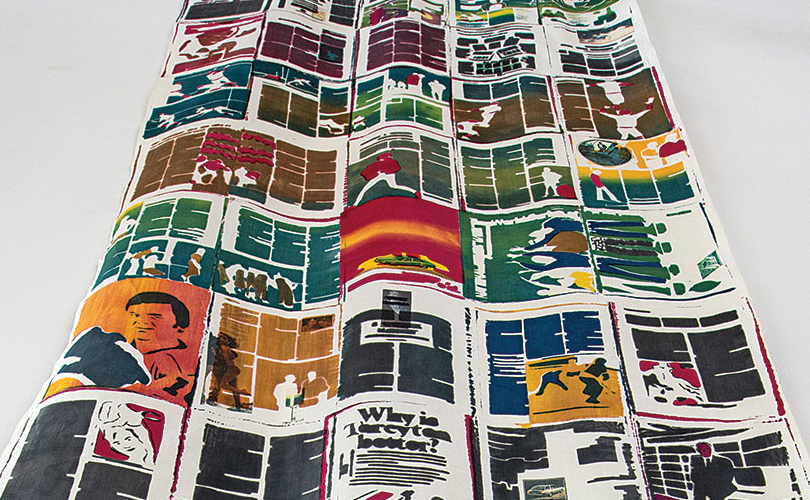
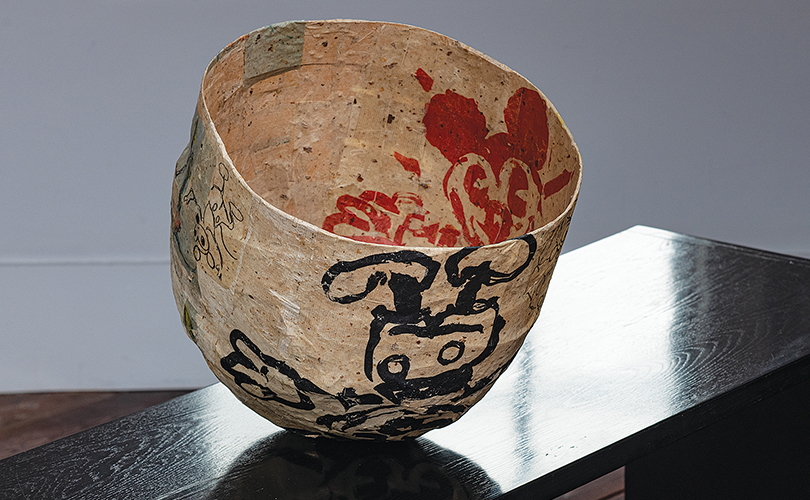
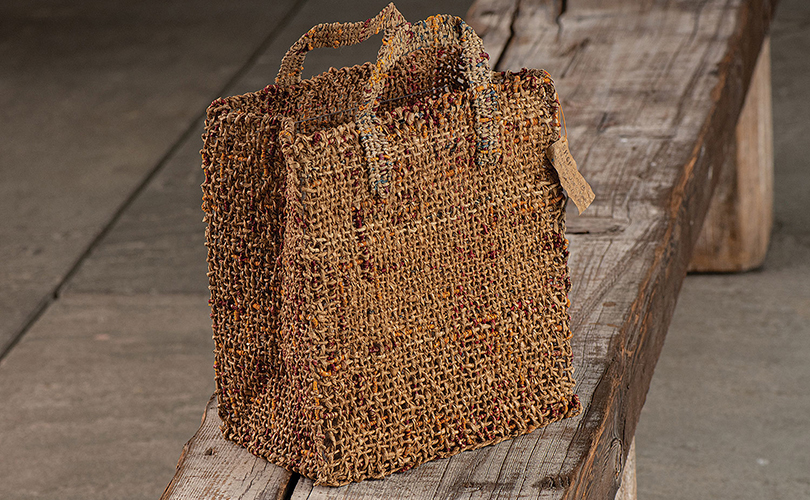
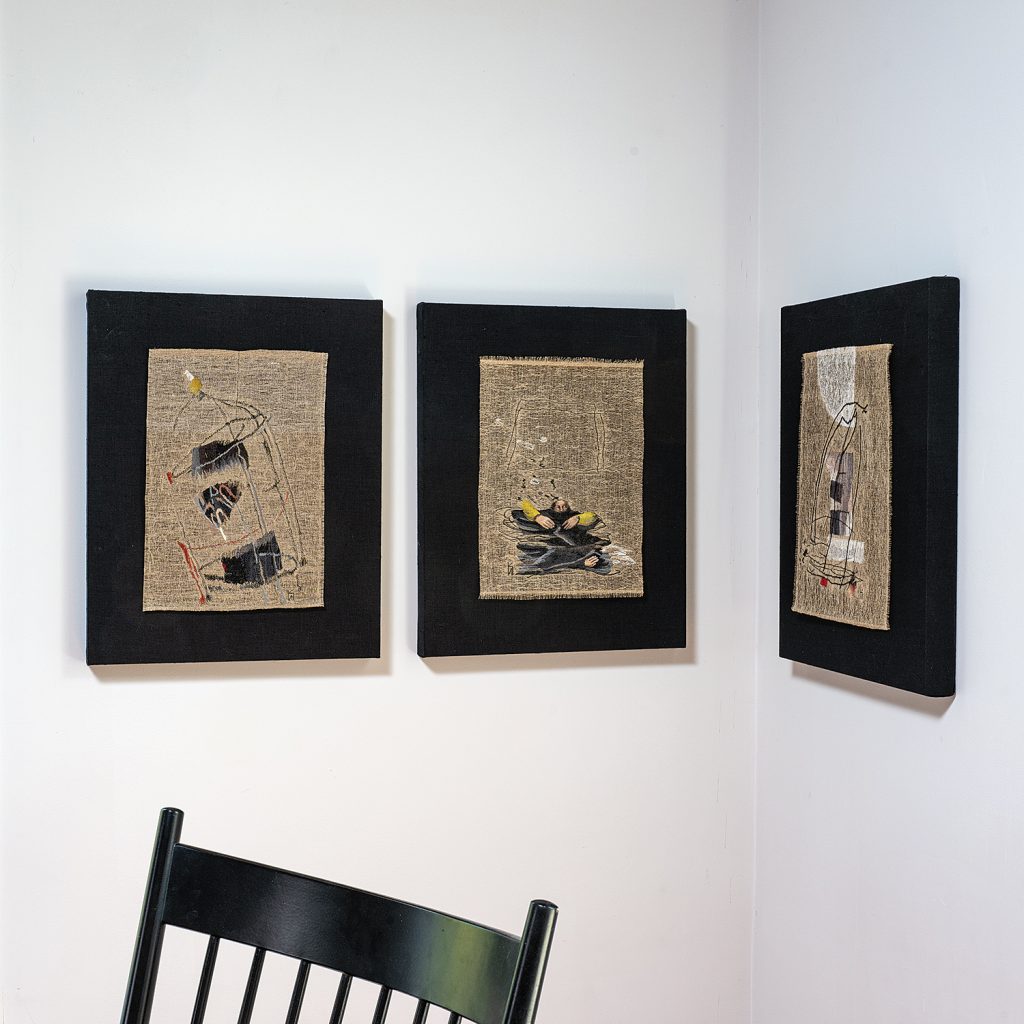
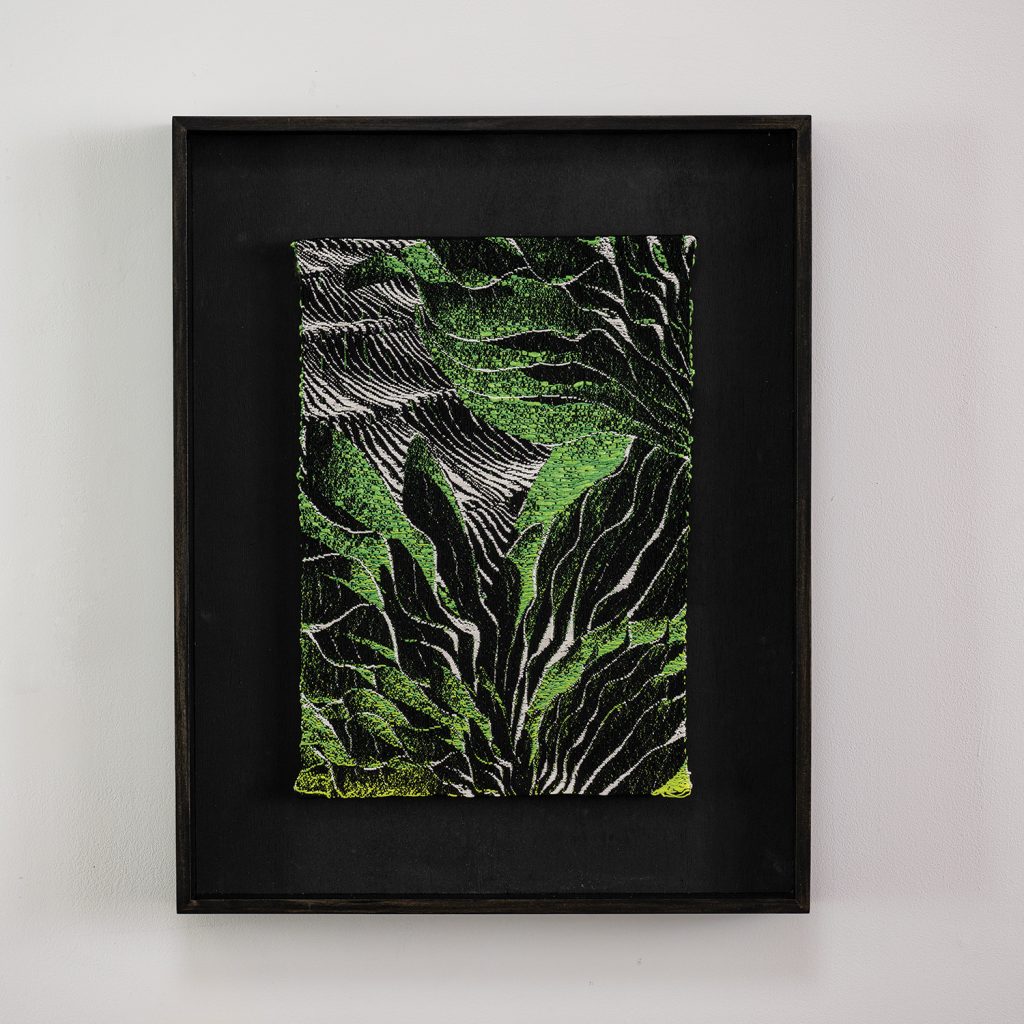
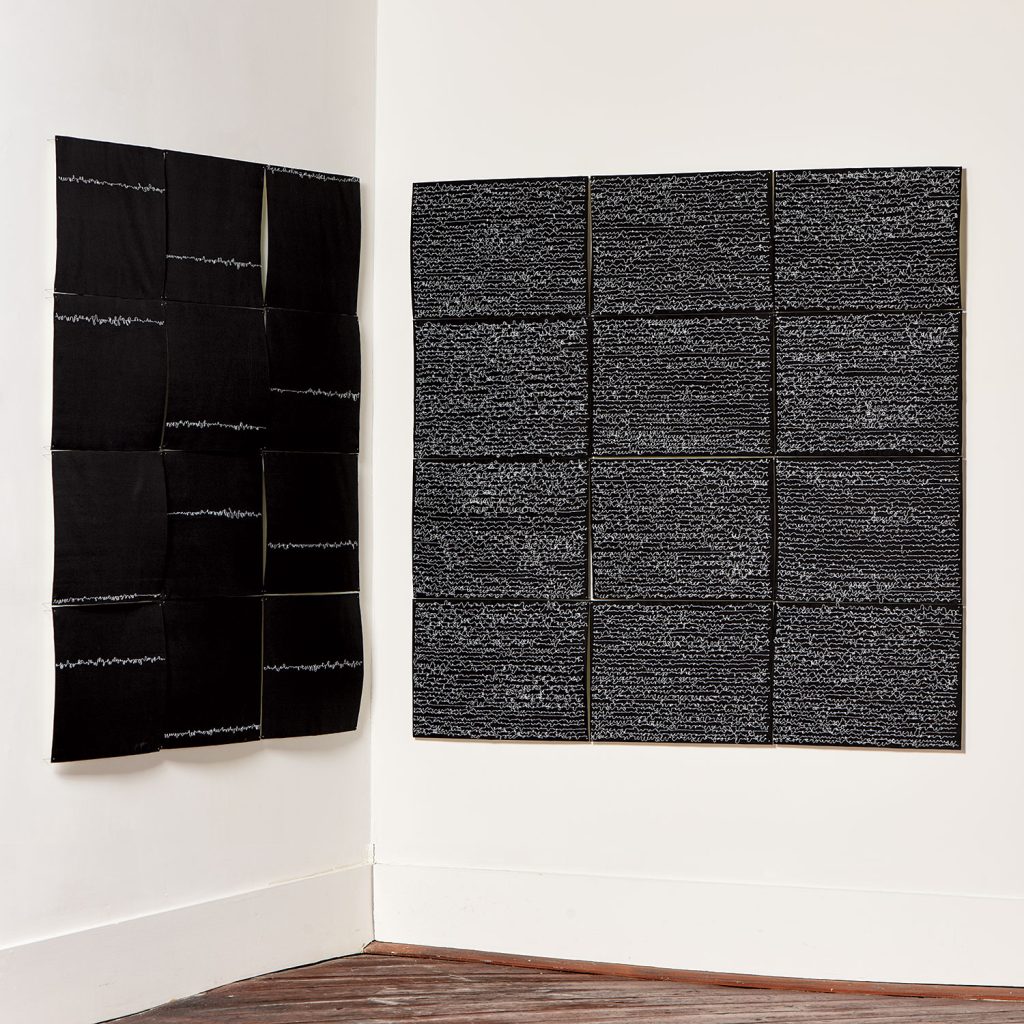
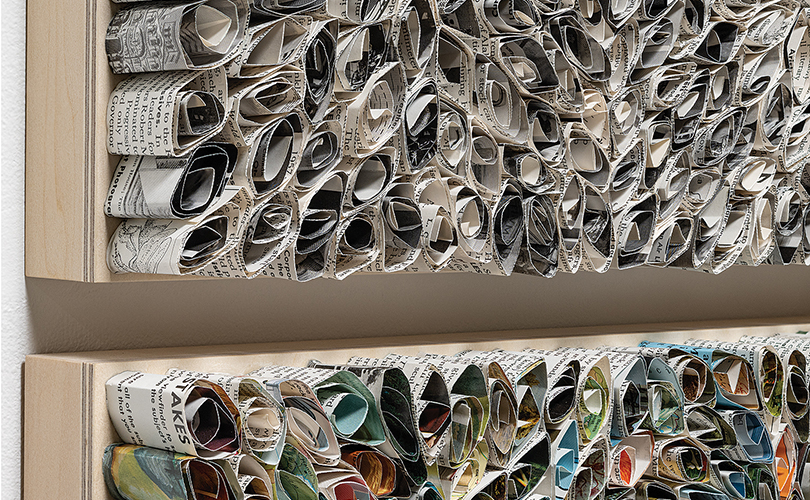
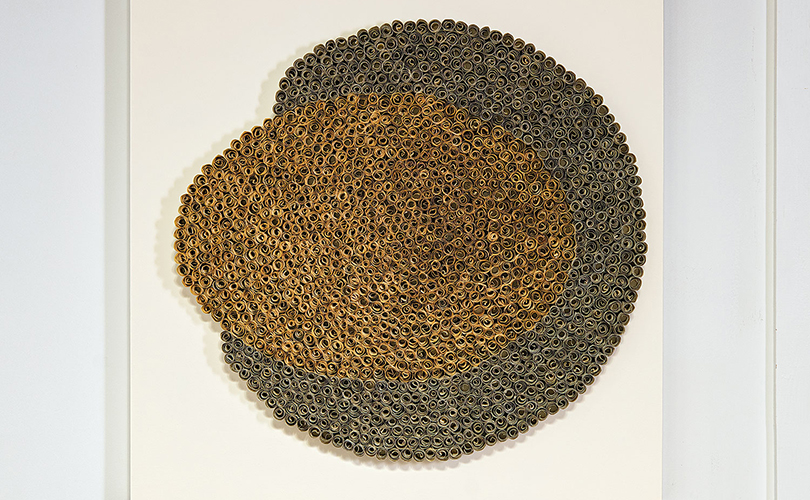
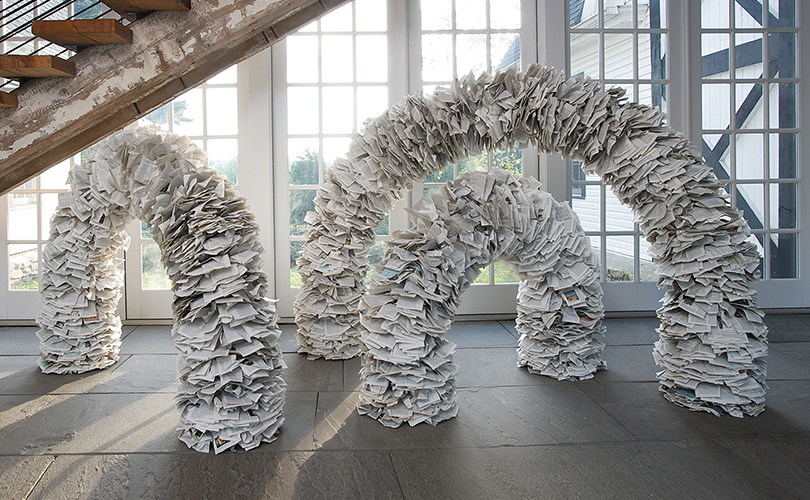
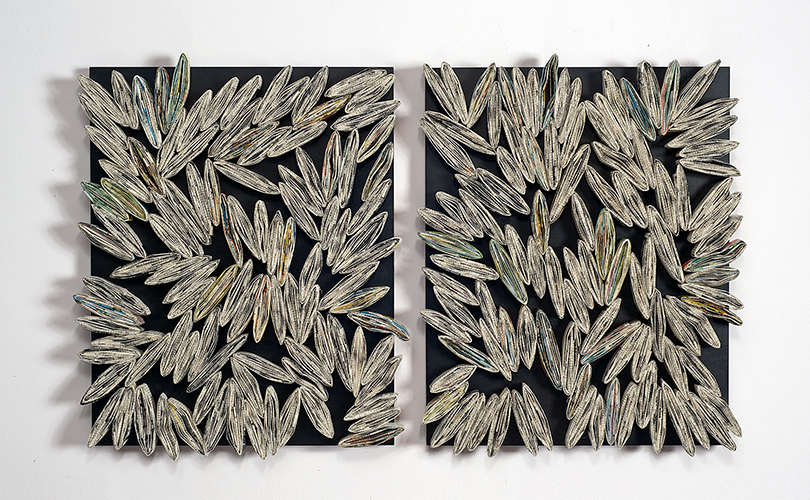
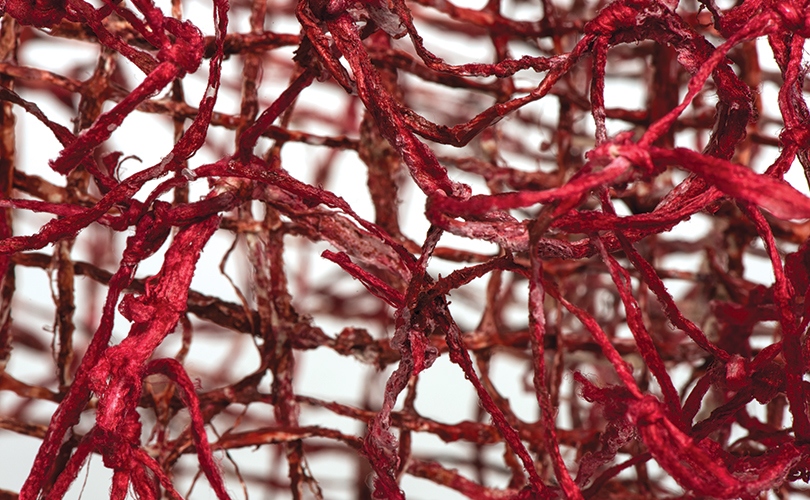
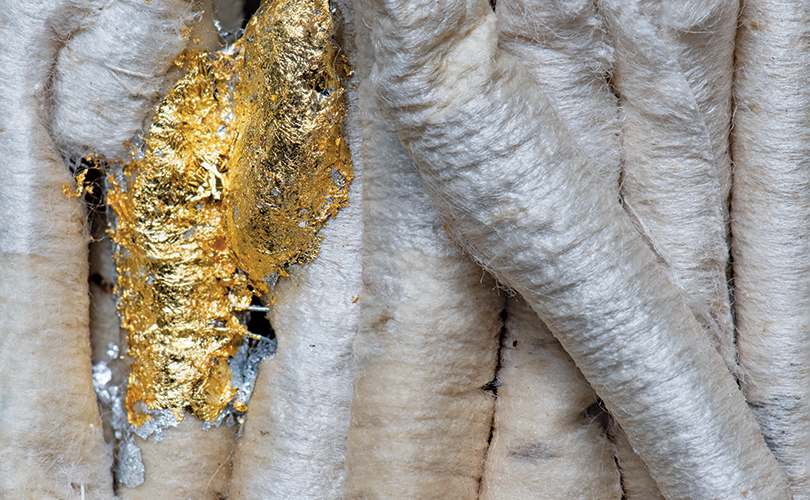
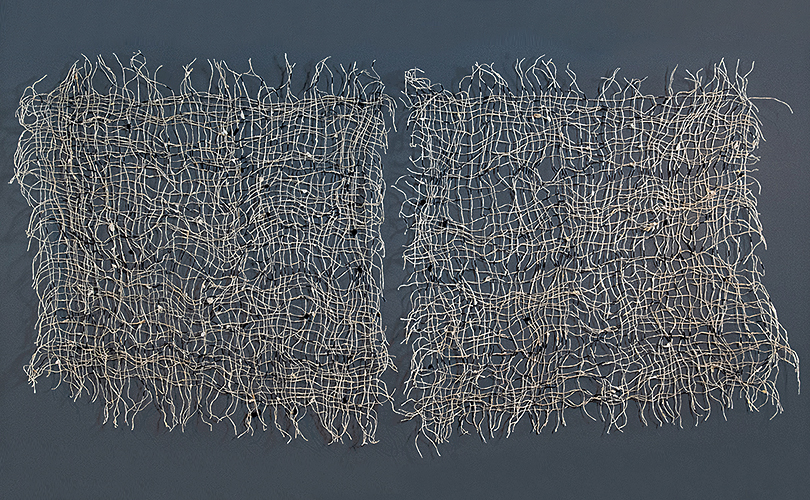
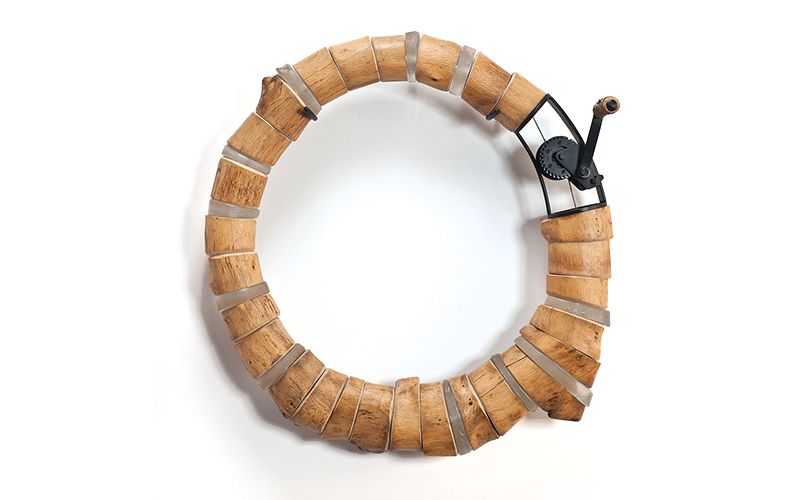
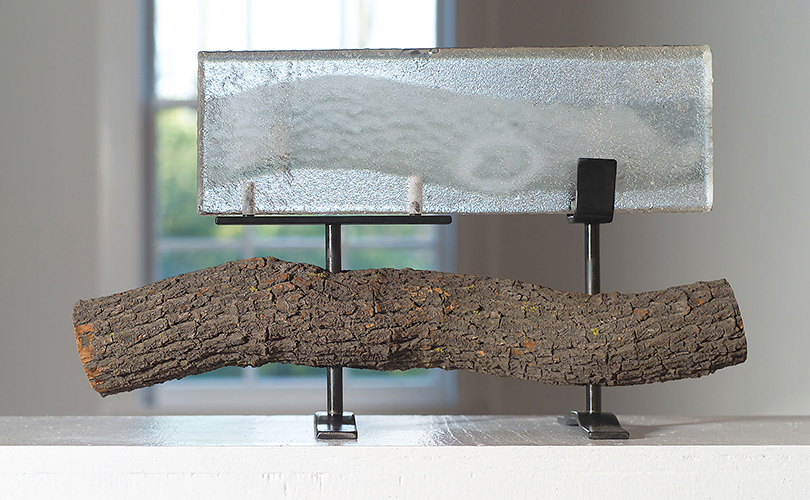
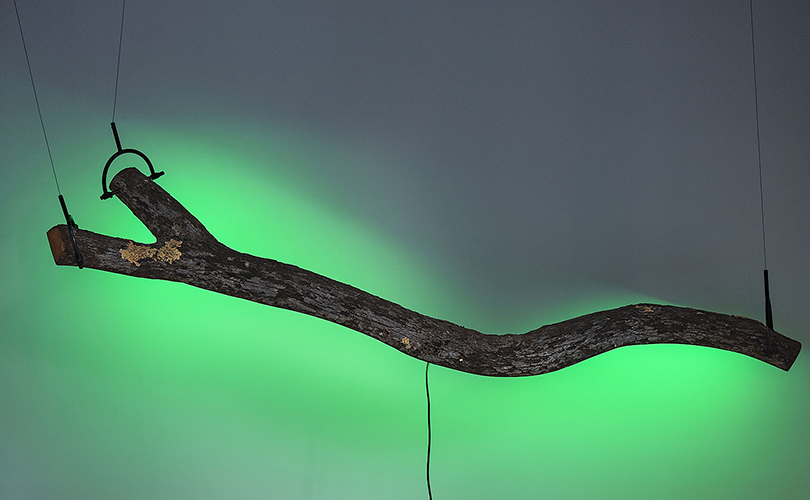
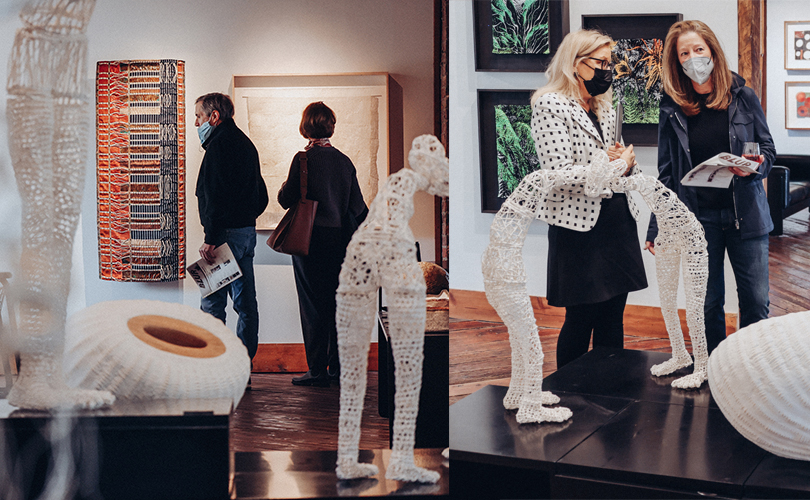
For Spring 2023, browngrotta arts is pleased to announce a wide-ranging exhibition of work by noted artists from around the world. Acclaim! Work by Award-Winning International Artists (April 29 – May 7) will highlight mixed media, fiber sculpture and contemporary textile artists artists creating and advancing the field of fiber arts now and throughout the last six decades, including Sheila Hicks, Dominic Di Mare, Kay Sekimachi, Jiro Yonezawa, Carolina Yrarrázaval and Ed Rossbach.

Awards by the dozen
The nearly 50 artists in Acclaim! Work by Award-Winning International Artists, have each achieved formal art acknowledgement in the form of an award or medal or selective membership. In the US, that may mean the award of a Gold Medal from the American Craft Council — 10 of the artists in Acclaim! belong to that group. In Canada, it means membership in the Royal Canadian Academy of the Arts, which three of our artists have achieved. The late masterweaver Peter Collingwood received an OBE, Order of the British Empire. Yeonsoon Chang of Korea was selected Artist of the Year by the Contemporary Art Museum in Seoul. In France, Simone Pheulpin was awarded the Grand Prix de la Création de la Ville de Paris. Grethe Sørensen of Denmark and Agneta Hobin of Finland received the Nordic Award in Textiles. Sheila Hicks of the US, was awarded the French Legion of Honor and a Lifetime Achievement Award from the International Sculpture Center; Helena Hernmarck received the American Institute of Architects, Craftsmanship Medal and the Prins Eugen Medal conferred by the King of Sweden for “outstanding artistic achievement.”

Results of recognition
Receiving an award can provide important affirmation for an artist. “There are no other large prizes in the UK for artists working in this medium,” says Jo Barker, winner of the Cordis Prize. “So what winning mostly felt like to me was a real validation of the career that I’ve had so far.” Such recognition can influence the direction of an artist’s work. Lia Cook’s Gold Medal from the American Craft Council provided her support for her process — particularly, she says, for “my continued interest in following the unexpected.” Once selected as Artist of the Year by the National Museum of Contemporary Art in Seoul, Korea, Yeonsoon Chang saw her textile work in the broader scope of contemporary art. “Objective recognition gave me courage to work and a sense of responsibility,” she says. For Chang, the award also meant expanded interest in her work from museums, galleries, and collectors. Winning Best Visual Arts Exhibition of the Year from the Circle of Critics of Art in Chile was a recognition of 40 years of work for Carolina Yrarrázaval and a confirmation for all those who believed in her work, clients, galleries and museums. More importantly, Yrarrázaval says, it was the first time that textile art received this award in Chile, placing it on par with all disciplines in visual arts. “It was not only a recognition of my personal contribution,” she says, “but also to this discipline, which for a long time was seen as a minor art.”

Art undeterred
After some years of being overlooked and undervalued, contemporary textile art has finally been embraced (again) in the last several years by a wider world of museums and galleries. The current focus on artists working in fiber finds complex, thoughtful and accomplished work – some produced today and some in years when gallery and museum attention was slight. “What may appear to be an explosion of textile producers, from a historical perspective, is an explosion of interest and awareness of a tradition that has always been important, deep and rich,” Adam Levine, director of the Toledo Museum of Art told Art News last year. (Katya Kazakina, The Art Detective: Textile Artists Are Back in the Public Spotlight in Museums and Galleries. Art Collectors? They’re Still Catching Up, February 4, 2022). in other words, even when out of popular favor, fiber artists were undeterred, continuing to create exceptional work.
A through line — then and now
The work in Acclaim! creates a through line from the movement’s early days to its current creative explosion, highlighting the importance of persistence and the benefits of recognition along the way. Fiber art’s revival in museums, galleries and with collectors is built upon the dedication and extraordinary talent of artists like those featured in Acclaim!
Join us next month
browngrotta arts
276 Ridgefield Road Wilton, CT 06897
Artist Reception and Opening: April 29, from 11am to 6 pm
Remaining Days
Sunday, April 30th: 11AM to 6 PM (40 visitors/ hour)
Monday, May 1st – Saturday, May 6th: 10AM to 5PM (40 visitors/ hour)
Sunday, May 7th: 11AM to 6PM [Final Day] (40 visitors/ hour)
Safety protocols
Eventbrite reservations strongly encouraged • No narrow heels please (barn floors)
Reserve a spot here: RESERVE