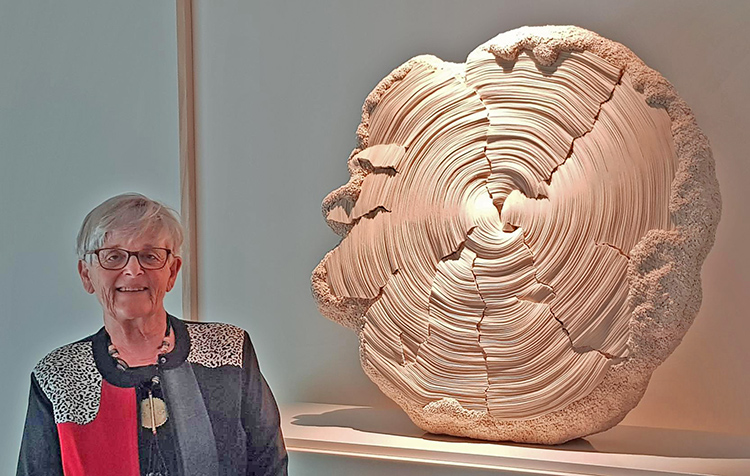
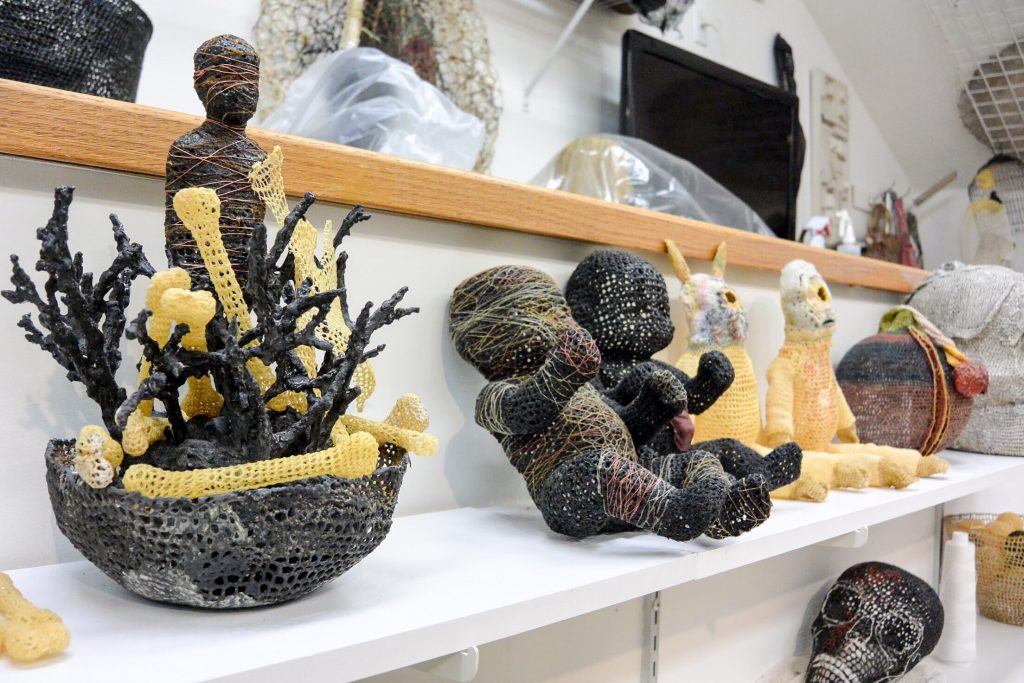
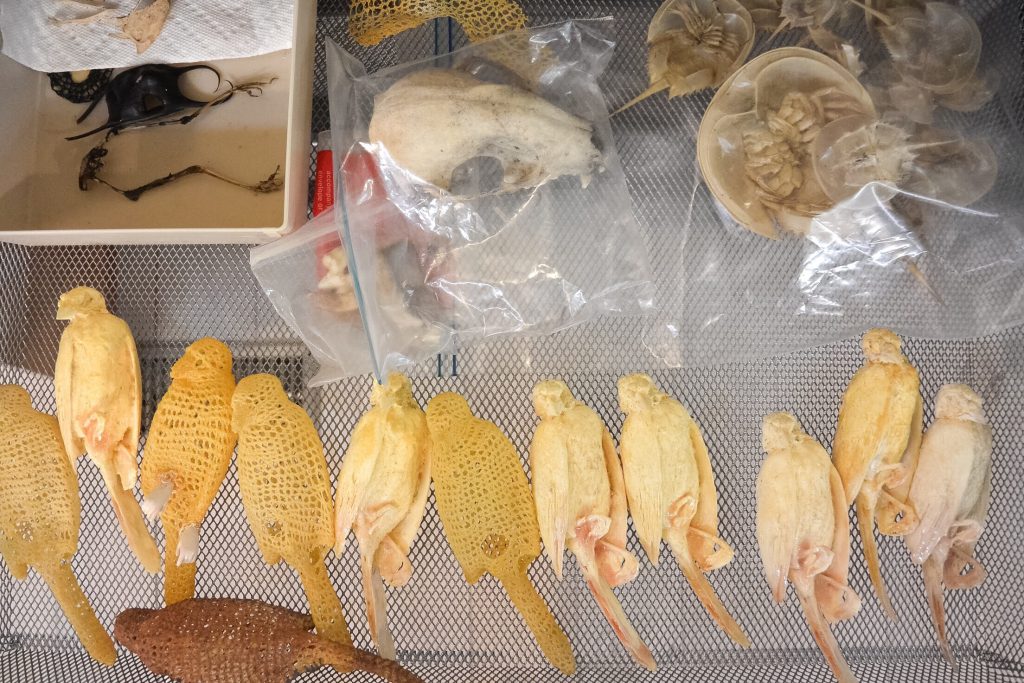
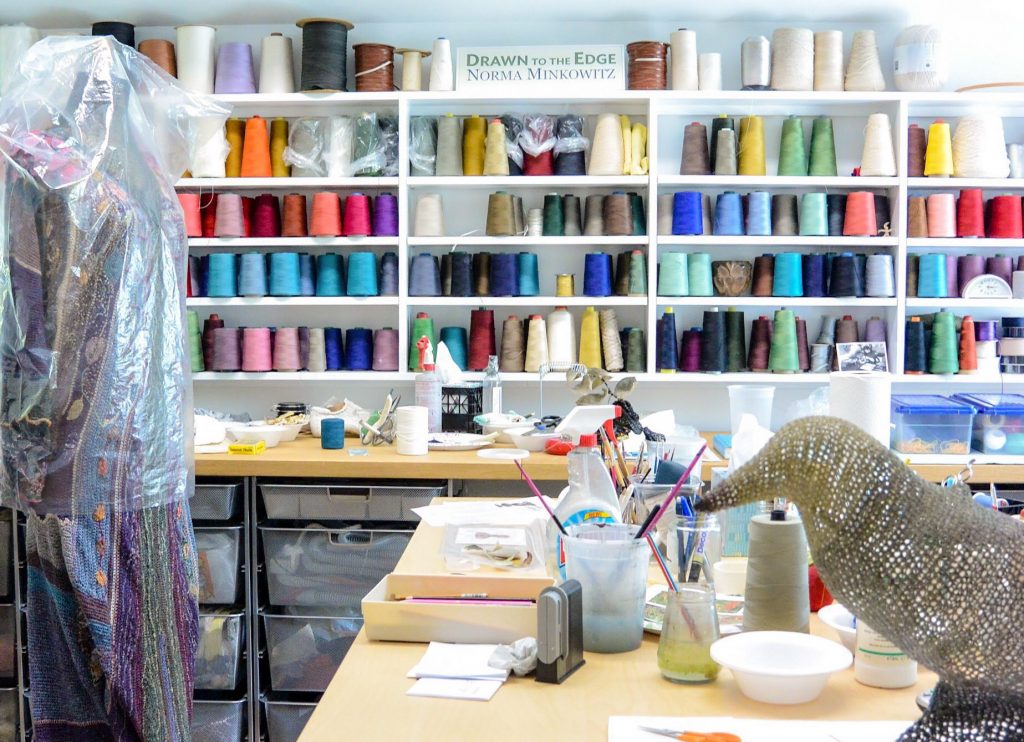
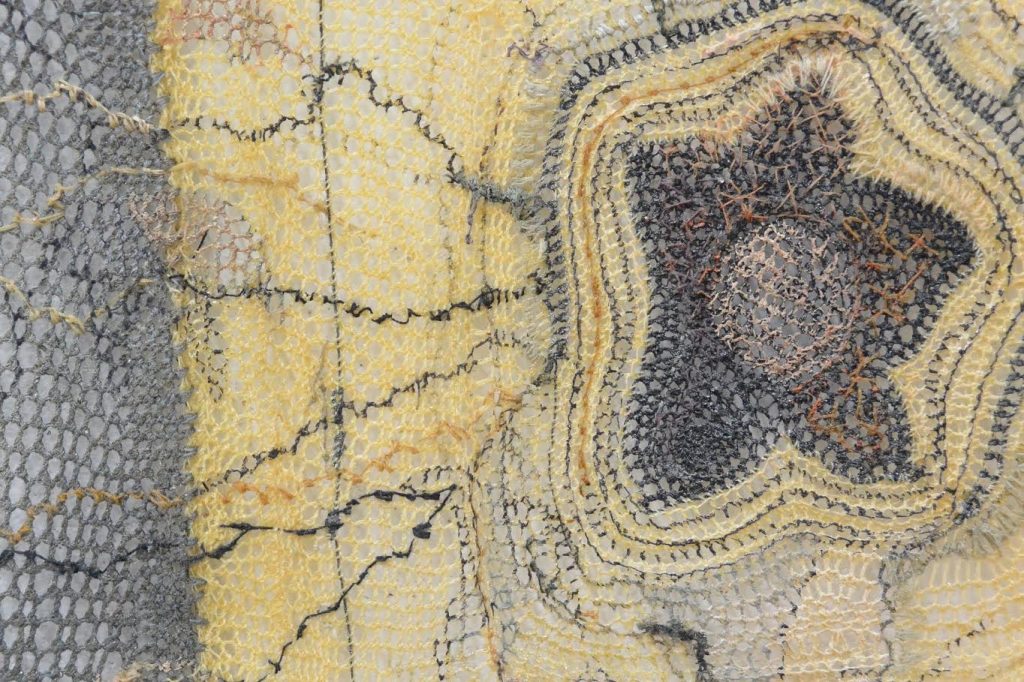
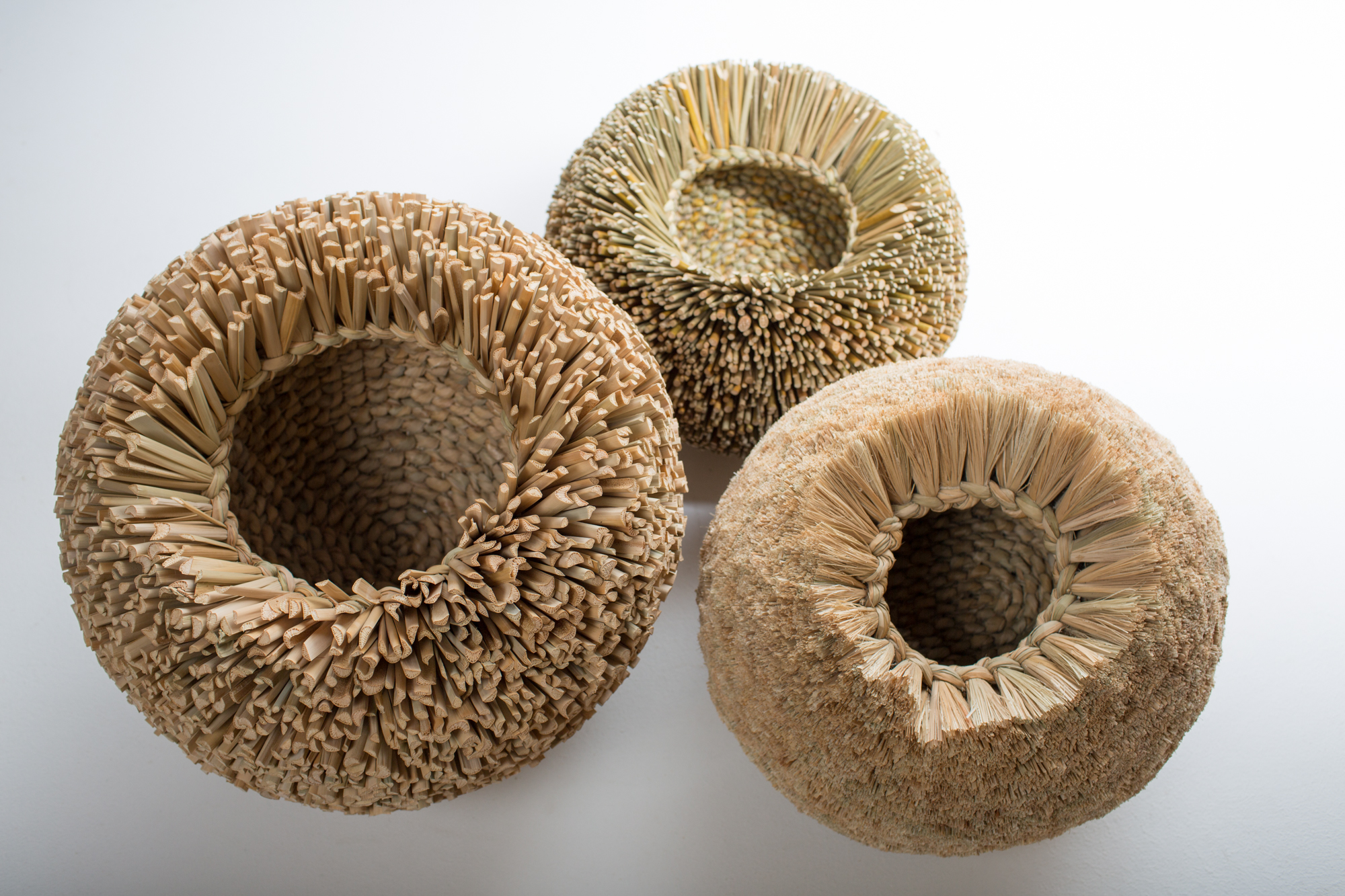
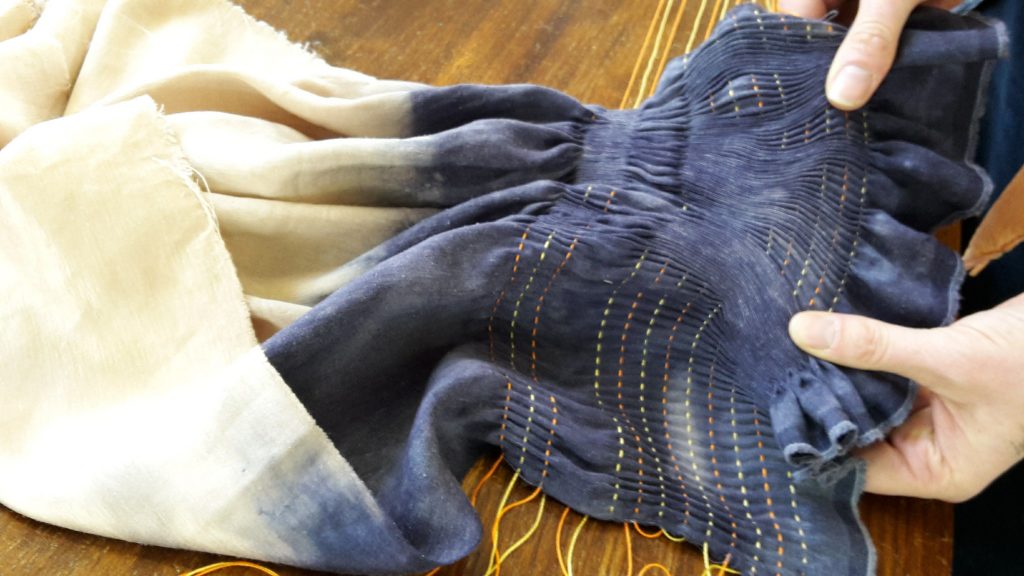
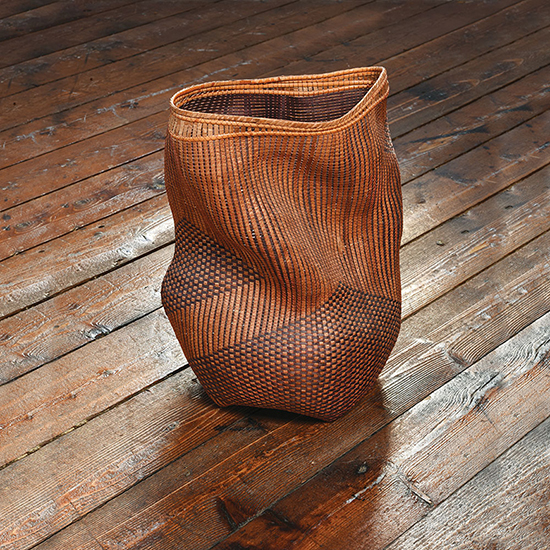
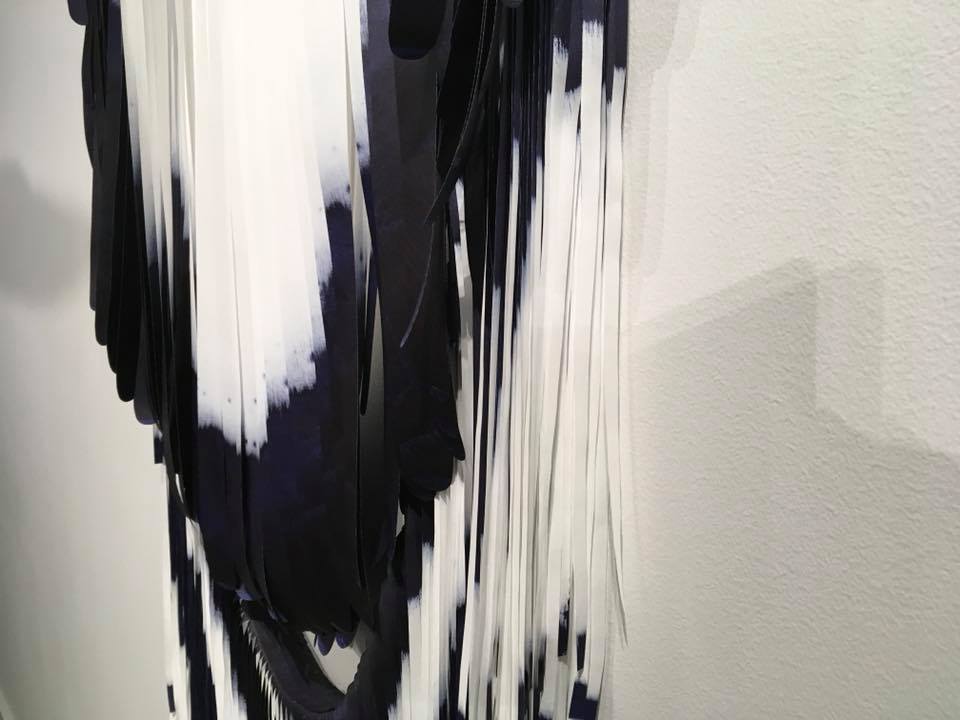
Simone Pheulpin at The Design Museum of London. Photo: Maison Parisienne
Last year, Artsy took a look at why old women had replaced young men as the “new darlings” of the art word. Its twofold explanation: as institutions attempt to revise the art-historical canon, passionate dealers and curators have seen years of promotion come to fruition and these artists have gained attention as blue-chip galleries search for new artists to represent among those initially overlooked.
Artsy points at Carmen Herrara, Carol Rama, Irma Blank, and Geta Brătescu and others to make its point. Mary Sabbatino, vice president at Galerie Lelong, is quoted as saying, “They’re fully formed artists, they’re mature artists, they’re serious artists. They’re not going to burn out as sometimes happens with younger artists…and normally the prices are far below the other artists of their generation, so you’re offering a value to someone.” Barbara Haskell, a curator at the Whitney Museum in New York, says museums everywhere are realizing that “there’s been a lopsided focus on the white male experience” in art history, and are working to correct that.”