
Contemporary fiber art is a fairly new art genre, having begun in the 1950s with experiments in weaving abstraction in the US and Europe and achieving its first international acknowledgment in the 1960s (Lausanne Biennial, Switzerland, 1962 and Woven Forms, US 1963). browngrotta arts has been involved in promoting international art textiles and fiber sculpture for nearly half of that history. As such, we have been remarkably fortunate to work with, been guided by and document the work of, pathbreakers and innovators in the field, including Lenore Tawney, Sheila Hicks, Lia Cook, Jin-Sook So and Ethel Stein. Each of these artists have played a significant role in more than one of our 50 publications, including Sheila Hicks, Joined by seven artists from Japan (#13) and Lenore Tawney: celebrating five decades of work (#28) and Beyond Weaving: International Arttextiles (#33). Three of them were the subject of artist monographs — Lenore Tawney: Drawings in Air (#1M); Lia Cook: In the Fold, Works from 1973-1977 (#2M); Ethel Stein: Weaver (#3M) one of them an artist’s focus — Focus: Jin-Sook So (#1F).
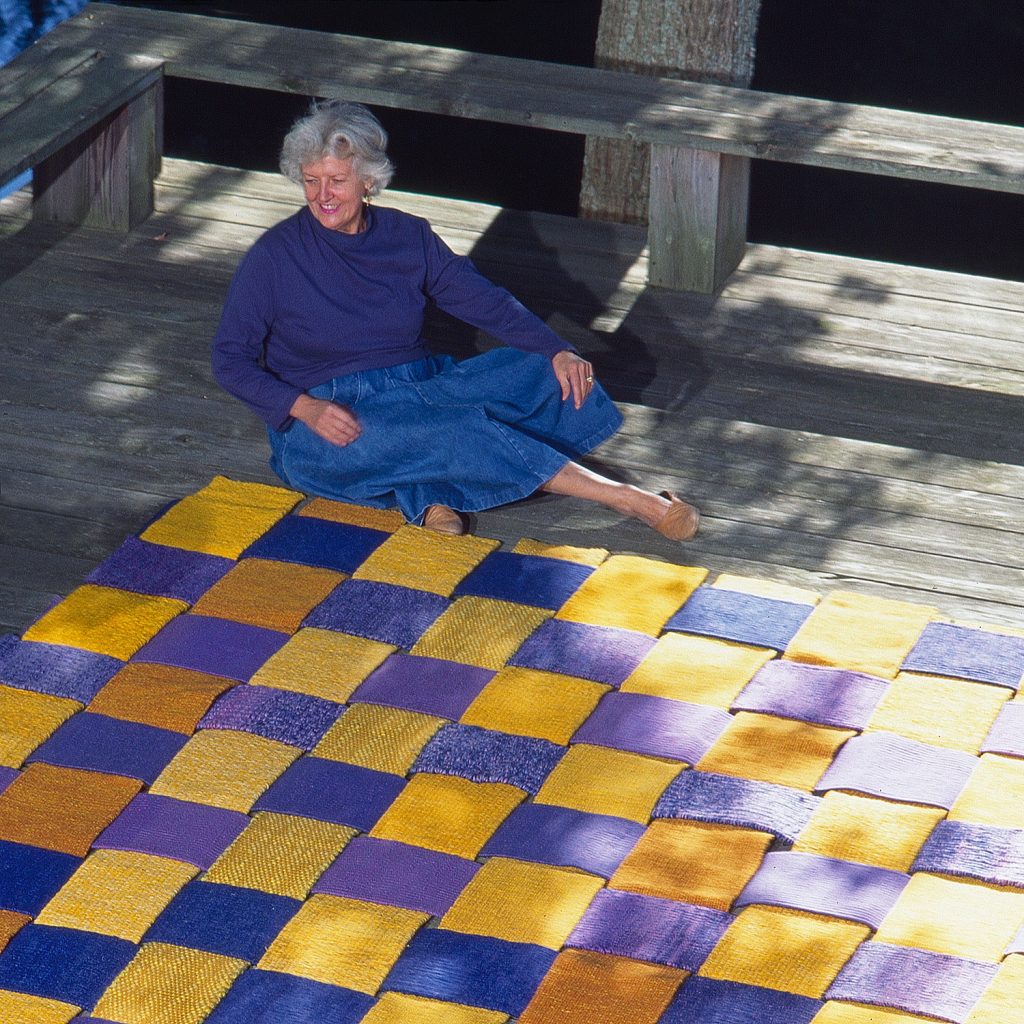

In 1996, we worked with Sheila Hicks on an exhibition that included seven artists from Japan, Masakazu Kobayashi and Naomi Kobayashi, Chiaki Maki, Toshio Sekiji, Hiroyuki Shindo, Chiyoko Tanaka and Jun Tomita. “The choice to show these works together was personal, ”Hicks wrote in Sheila Hicks, Joined by seven artists from Japan (#13). She chose our space in Connecticut, intentionally, noting that the in the Connecticut landscape, “it would be easy to contemplate their inner messages or, at least, to discover their structural wizardry.” Hicks had shown these artists’ works to friends, and noted that, “[a] harmonious dialogue between their work and my own began to develop naturally.” We were assisted in installing the exhibition, which Hicks designed, by Cara McCarty, then at the St. Louis Art Museum and Mathilda McQuaid, then at MoMA, both now at the Cooper Hewitt. The exhibition was well received. It led to others in Paris and Jerusalem and a follow up in Wilton (Traditions Transformed (#22). Ultimately, Hicks and six of the artists appeared in the major MoMa survey: Surface and Structure: Contemporary Japanese Textiles (1998-99), curated by McQuaid and McCarty, which highlighted the revolution that had occurred in the creation of textiles during the 90s. Hicks has continued to receive international acclaim and has been the subject of numerous solo exhibitions — Israel Museum, Jerusalem;, Museum of Nebraska Art, Kearney; Contemporary Art Center of Virginia, Virginia Beach; Bard Graduate Center, New York, NY; Addison Gallery of American Art, Andover, Massachusetts, Joslyn Art Museum Omaha, Nebraska; Museo Amparo, Puebla, México; Centre Pompidou, Paris, France; Municipal Cultural Center Gallery, Kiryu, Gunma, Japan; Museo Chileno de Arte Precolombino, Santiago, Chile and The Bass, Miami Beach, Florida.
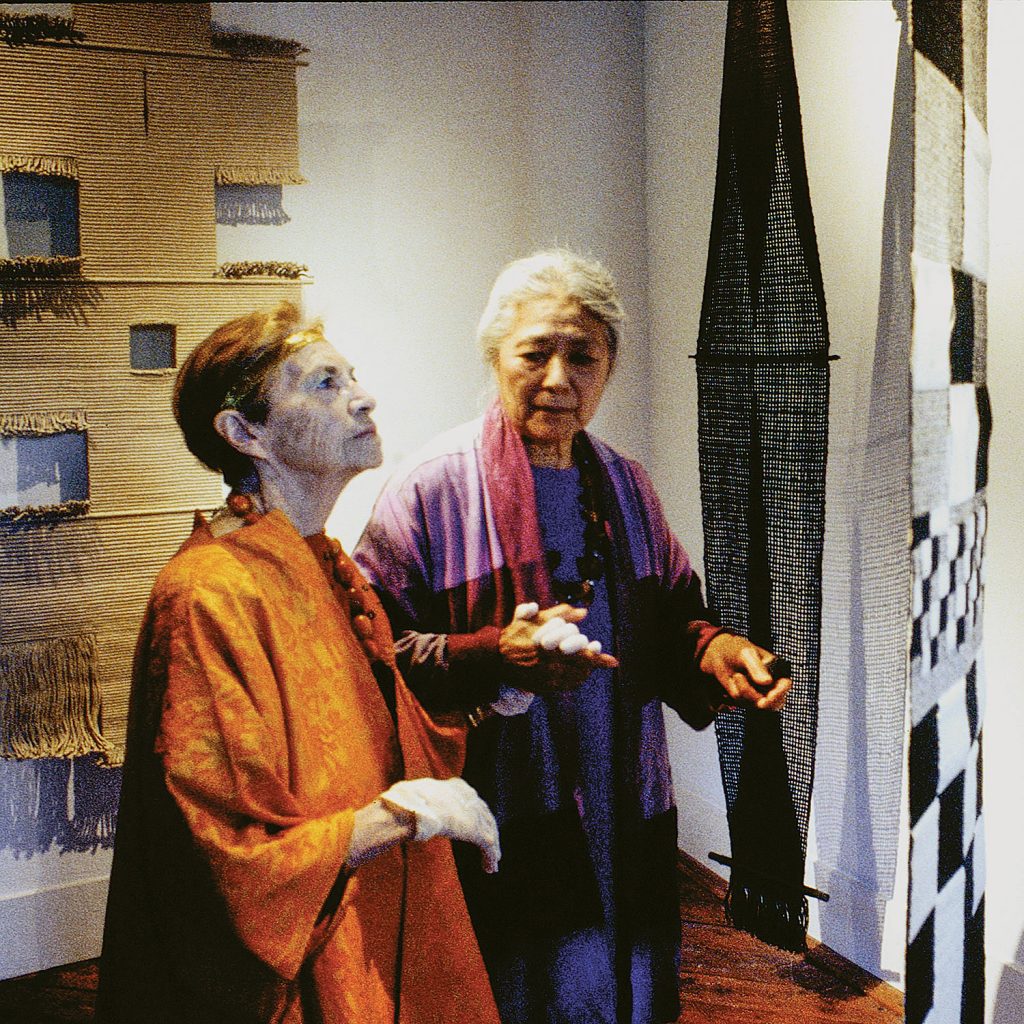

Our representation of Lenore Tawney was equally meaningful to us personally and influential to browngrotta arts’ evolution. When we decided to move our home and exhibition space, a major factor was finding a room with a ceiling high enough to exhibit a Tawney Cloud. In 2000, we were able to make that happen, when we celebrated five decades of Tawney’s work (#28). The exhibition illuminated the breadth of Tawney’s vision — including woven forms, collage, assemblage and drawings. Many of the works — created in the 50s, 60s, 70s, 80s and 90s — had rarely been exhibited before. The catalog also included never-published excerpts from Tawney’s journals and an essay by Bauhaus scholar, Sigrid Wortmann Weltge, who authored Bauhaus Textiles: Women Artists and the Weaving Workshop (Thames & Hudson 1998). We followed it with a monograph (#1M) exploring Tawney’s Drawings in Air series — ruled drawings on graph paper that predated systemic drawings of Minimalists like Sol Lewitt, and served as the impetus for three-dimensional thread sculptures three decades later. “I did some of these drawings that look so much like threads that people think they are threads,” Tawney wrote, “but I didn’t do them with that in mind …. It’s like meditation — you have to be with the line all the time—you can’t be thinking of anything.”
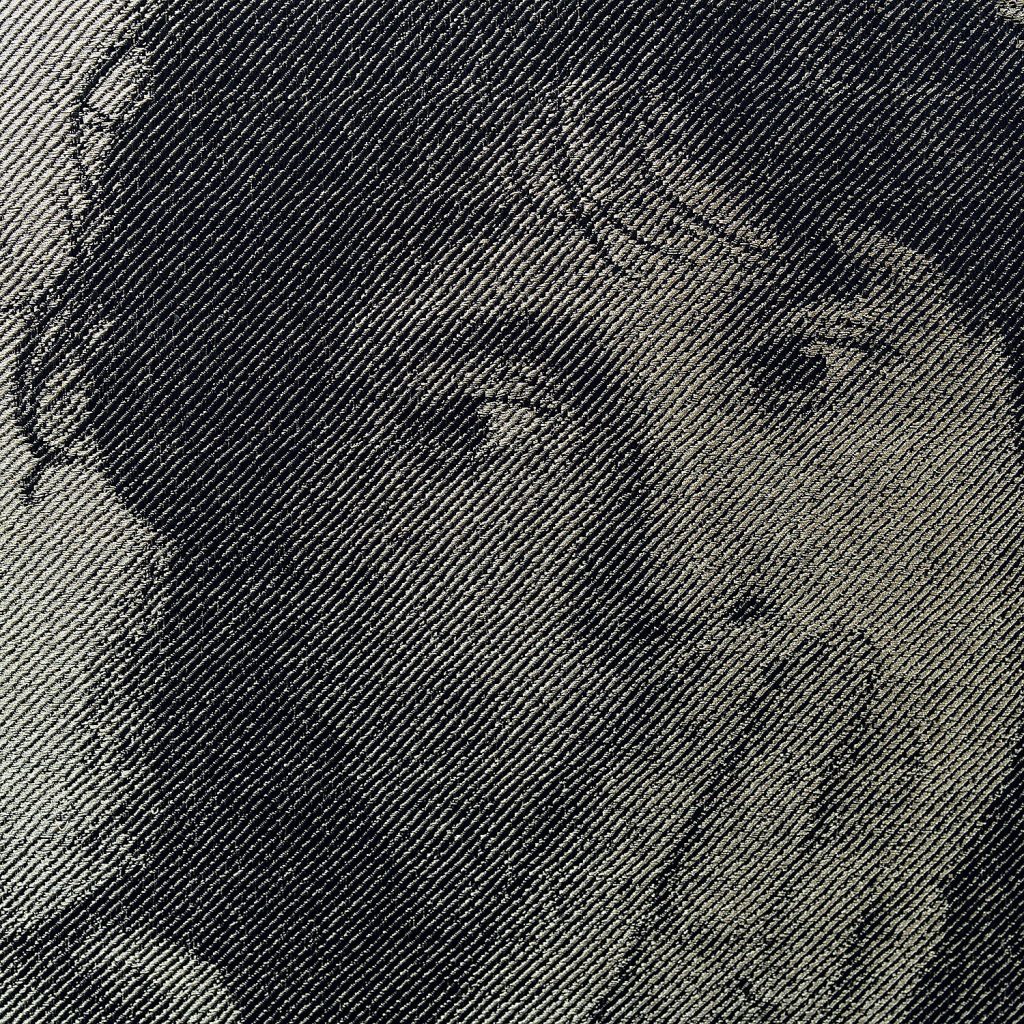

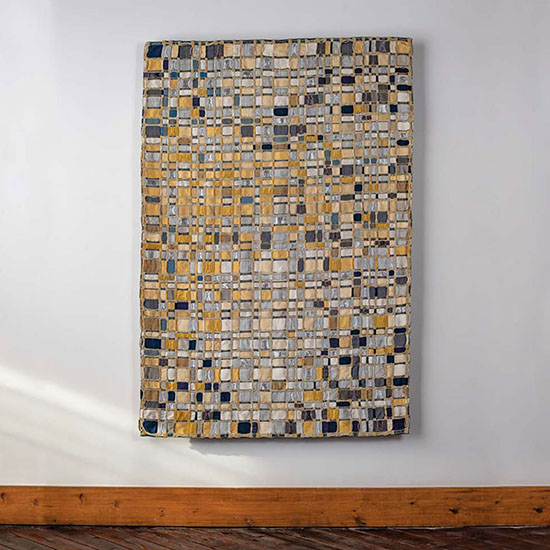
Like Hicks and Tawney, Lia Cook was a participant in the Lausanne Biennial, first in 1973, just after she completed her Master’s degree at University of California, Berkeley in Art & Design. Since that time Cook has reinvented her art practice several times, first creating macroscopic imagery of woven structures, then exploring image of draped fabrics incorporating hand-painted rayon warp threads. In the 90s, she began weaving photographic compositions and then, in 2000s, she began taking measurements of brain waves as people looked at photos and then at woven images, integrating them into her work as well. “Cook’s work defies the ocular-centricity of Western art by overturning the hierarchy of the senses,” wrote Deborah Valoma in our monograph on Cook (#2), “and repositioning the sense of touch in the foreground …. Cook asks her viewers to ’see’ the experience of touch — to imagine the sensations of touch through the visual experience of seeing.” The uniquely tactile experience created by Cook’s work has been featured in dozens of exhibitions worldwide, many of them solo exhibitions. Her work is found in dozens of museum collections, including that of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, the De Young Museum, Minneapolis Institute of Art and the Art Institute of Chicago. Su Series, Cook’s work that is featured in our Volume 50 exhibition in September, is composed of 32 woven identical images of her face as a child superimposed with empirical data from her neuroscience research, created on a Jacquard computerized handloom. Each individual image is translated and altered through different weaving structures, provoking from the viewer a subtle and sometimes dramatic variation in emotional reaction..
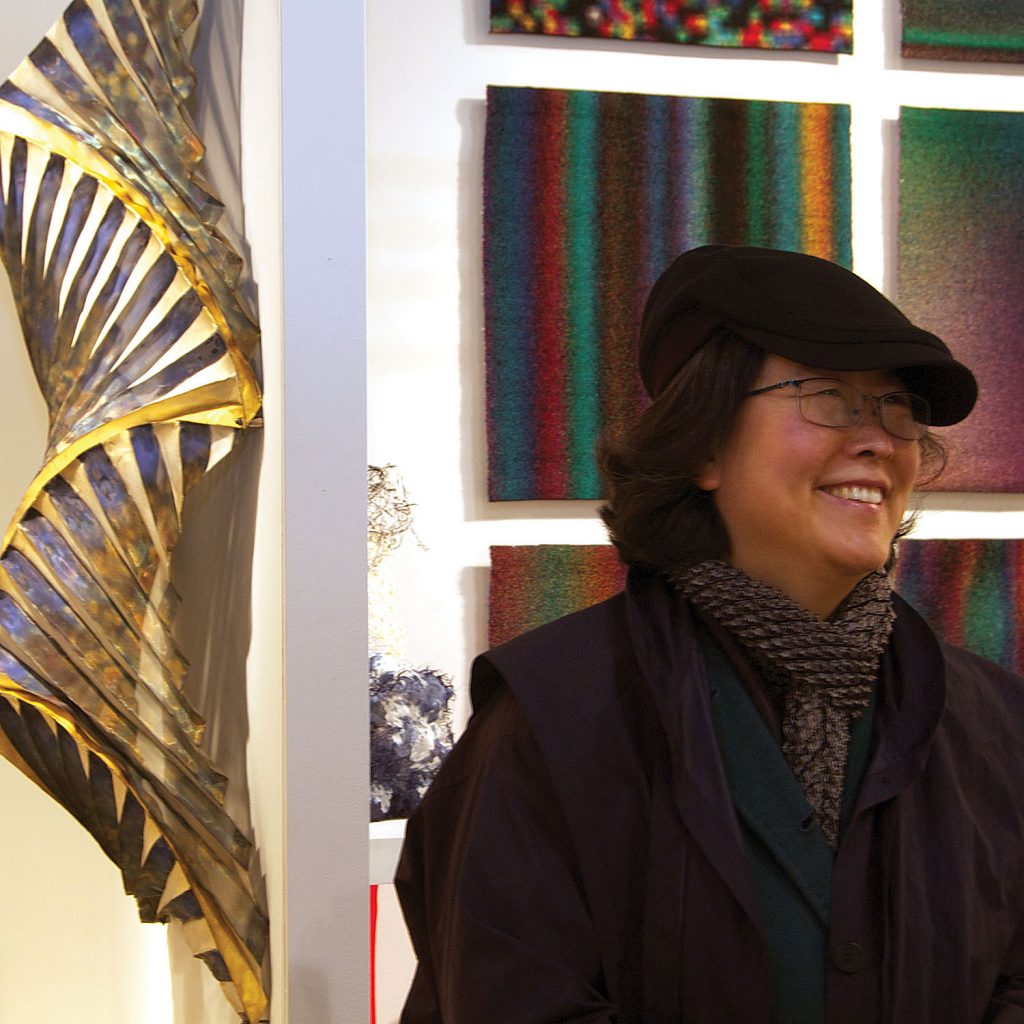

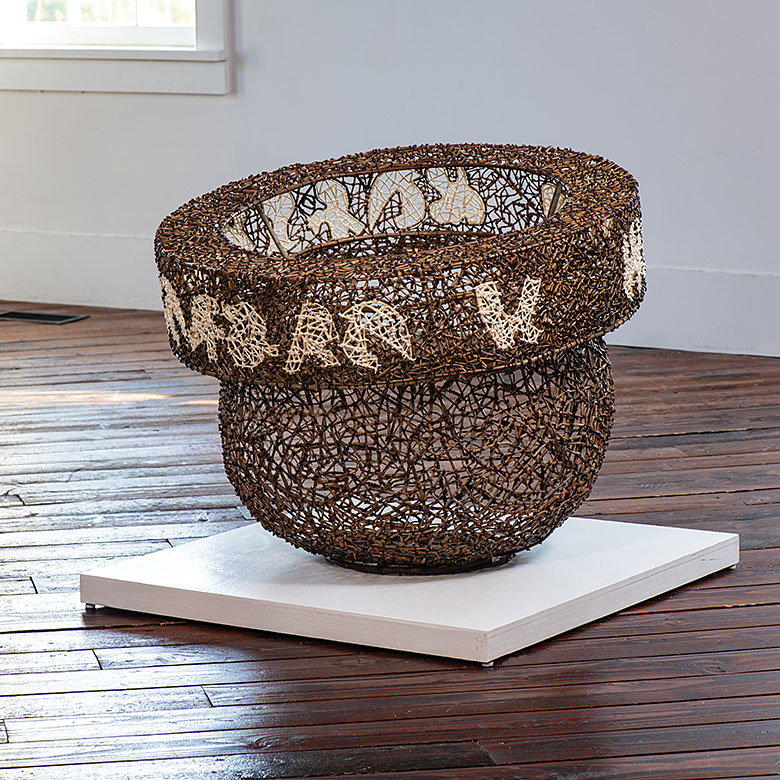
Jin-Sook So is another innovator with an international presence who has moved from working with wool to working with organza, and for the last two decades, stainless steel and copper mesh. For the Lausanne Biennial in 1989, she worked directly with flat steel mesh, pleated manually and colored black and blue and brown with a blow torch. By the mid 90s, “her form language had become more distinct and more consistently constructivist,” Kerstin Wickman, Professor of History of Design and Craft at Konstfack, University College of Arts Crafts and Design in Stockholm wrote in Focus: Jin-Sook So (#1F). “In spite of their minimal and precise shapes, [her] boxes, as well as the folded constructions, impart a softness and a sensuality created by the illusionary ‘movements,’ the variations and the poetic surfaces.” Born in Korea, she studied in Japan and New York and lived nearly three decades in Sweden. So’s work is influenced by each of these experiences. The shimmering gold and blue and black of her constructed works reflect light in ways that recall urban landscapes in New York and Sweden’s remarkable, diffused light. More recent works, including the bowl shapes that will appear in Volume 50, link back to her childhood and tie more directly to the past, evoking a pool of memories, of stories told and feelings expressed. So’s work has been exhibited in Asia, Scandinavia, Japan and the US.
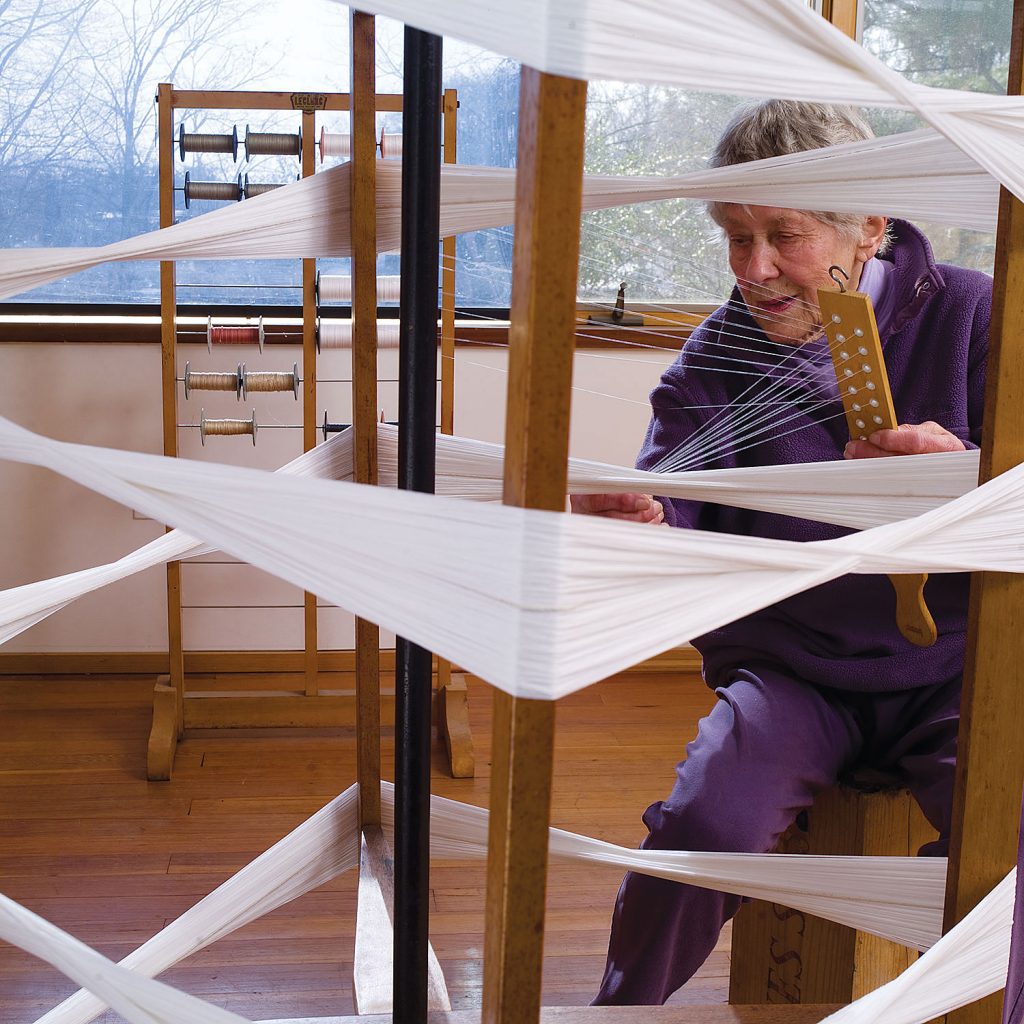

A contemporary and colleague of Tawney’s in New York and also invited to the Lausanne Biennale, when Ethel Stein began weaving in the 60s, she took a different tack than the textile artists creating large, dimensional and off-loom works. Instead, despite her background as a sculptor, she worked “counter trend” in Jack Lenor Larsen’s words, her weavings remaining small and flat. She immersed herself in difficult and exacting cloth traditions, using an ancient drawloom which was replaced 200 years ago by the Jacquard loom. Our monograph, Ethel Stein: Weaver (#3M), followed Stein through her early art instruction, work as a sculptor and creation of damasks, double weaves and feathery ikats. At 96, the fresh expressions that Stein created from her explorations into ancient techniques brought her well-deserved recognition in a one-person exhibition, Ethel Stein: Master Weaver, at the Art Institute of Chicago in 2014, which featured large photographic images and works from Focus. The delay, the Art Institute’s material surmised, was due, in part, to the fact that,“her weavings look deceptively simple, with the result that only those well versed in the craft she practices can truly appreciate the sophistication of Stein’s work and the magnitude of her accomplishment.”
Join us in September for Volume 50: Chronicling Fiber for Three Decades (Artists Opening: September 12, 2020) http://www.browngrotta.com/Pages/calendar.php. More information to combine on how we will combine art viewing and safe practice.
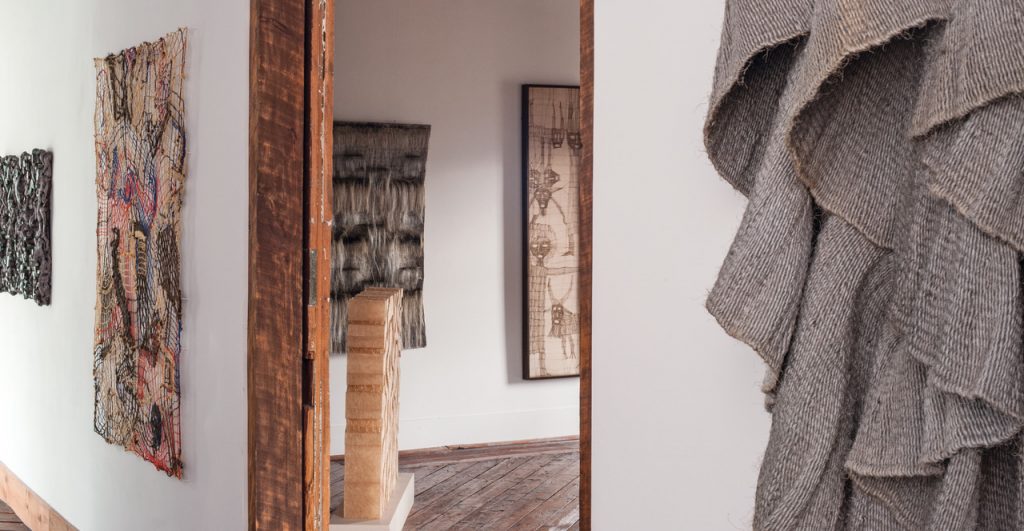
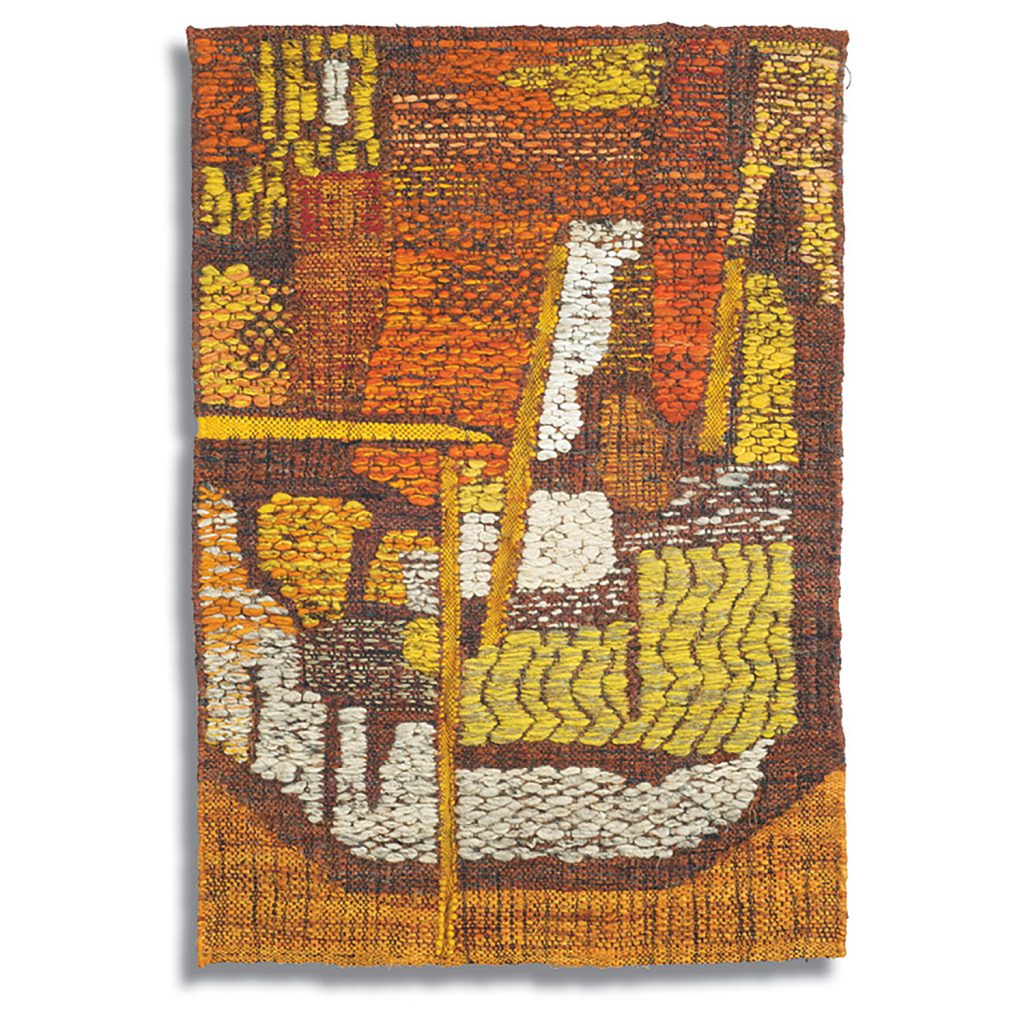
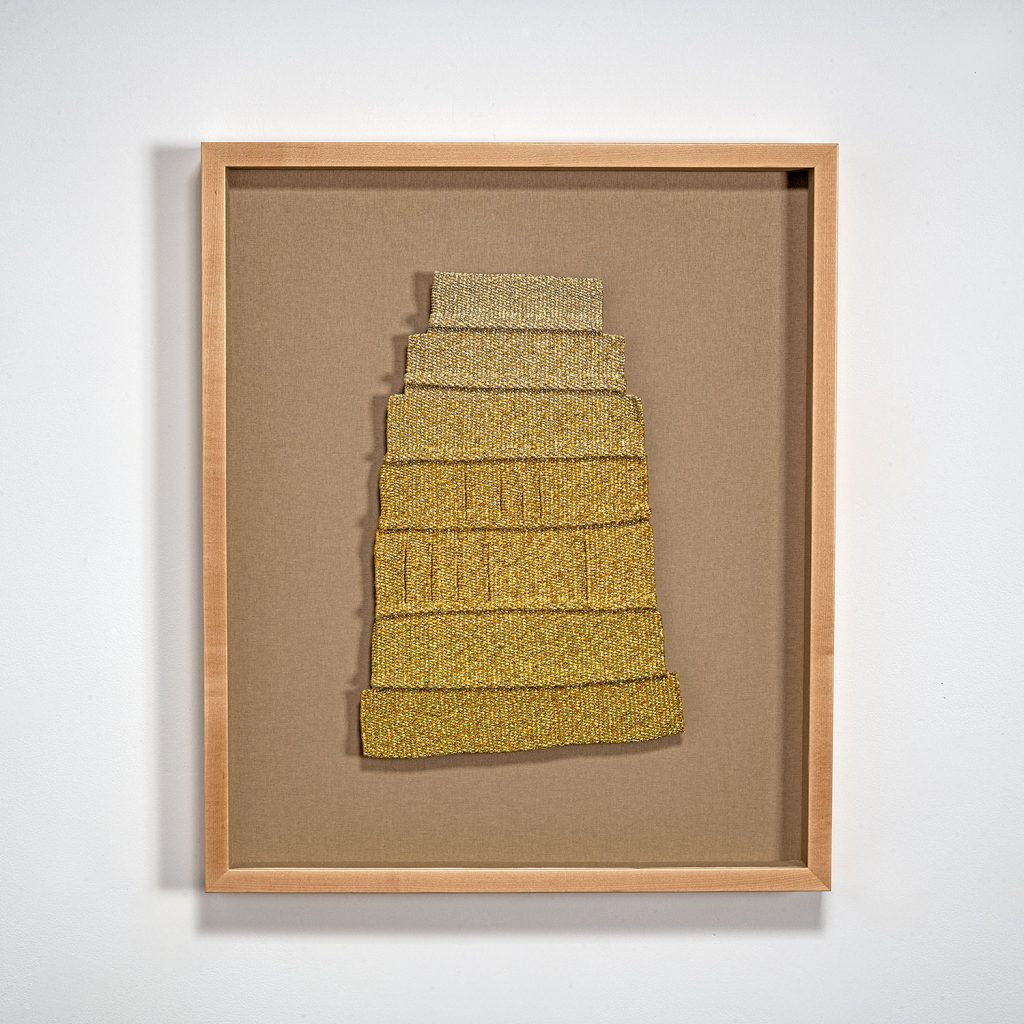
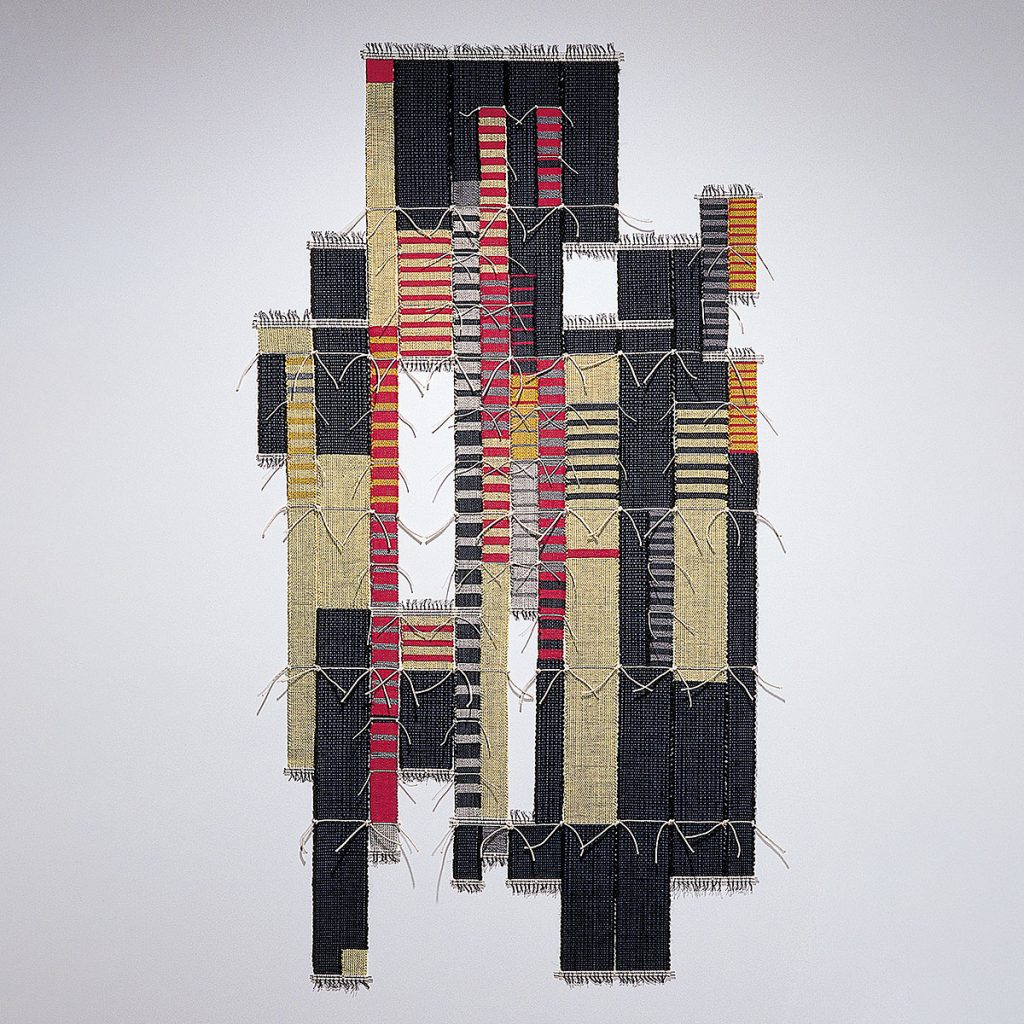


































Art & Identity: A Sense of Place
In our 2019 Art in the Barn exhibition, we asked artists to address the theme of identity. In doing so, several of the participants in Art + Identity: an international view, wrote eloquently about places that have informed their work. For Mary Merkel-Hess, that place is the plains of Iowa, which viewers can feel when viewing her windblown, bladed shapes. A recent work made a vivid red orange was an homage to noted author, Willa Cather’s plains’ description, “the bush that burned with fire and was not consumed,” a view that Merkel-Hess says she has seen.
The late Micheline Beauchemin traveled extensively from her native Montreal. Europe, Asia, the Middle East, all influenced her work but depictions of the St. Lawrence River were a constant thread throughout her career. The river, “has always fascinated me,” she admitted, calling it, “a source of constant wonder” (Micheline Beauchemin, les éditions de passage, 2009). “Under a lemon yellow sky, this river, leaded at certain times, is inhabited in winter, with ice wings without shadows, fragile and stubborn, on which a thousand glittering lights change their colors in an apparent immobility.” To replicate these effects, she incorporated unexpected materials like glass, aluminum and acrylic blocks that glitter and reflect light and metallic threads to translate light of frost and ice.
Mérida, Venezuela, the place they live, and can always come back to, has been a primary influence on Eduardo Portillo’s and Maria Davila’s way of thinking, life and work. Its geography and people have given them a strong sense of place. Mérida is deep in the Andes Mountains, and the artists have been exploring this countryside for years. Centuries-old switchback trails or “chains” that historically helped to divide farms and provide a mountain path for farm animals have recently provided inspiration and the theme for a body of work, entitled Within the Mountains. Nebula, the first work from this group of textiles, is owned by the Cooper Hewitt Museum.
Birgit Birkkjaer’s Ode for the Ocean is composed of many small woven boxes with items from the sea — stones, shells, fossils and so on — on their lids. ” It started as a diary-project when we moved to the sea some years ago,” she explains. “We moved from an area with woods, and as I have always used materials from the place where I live and where I travel, it was obvious I needed now to draw sea-related elements into my art work.”
“I am born and raised in the Northeast,” says Polly Barton, “trained to weave in Japan, and have lived most of my life in the American Southwest. These disparate places find connection in the woven fabric that is my art, the internal reflections of landscape.” In works like Continuum i, ii, iii, Barton uses woven ikat as her “paintbrush,” to study native Southwestern sandstone. Nature’s shifting elements etched into the stone’s layered fascia reveal the bands of time. “Likewise, in threads dyed and woven, my essence is set in stone.”
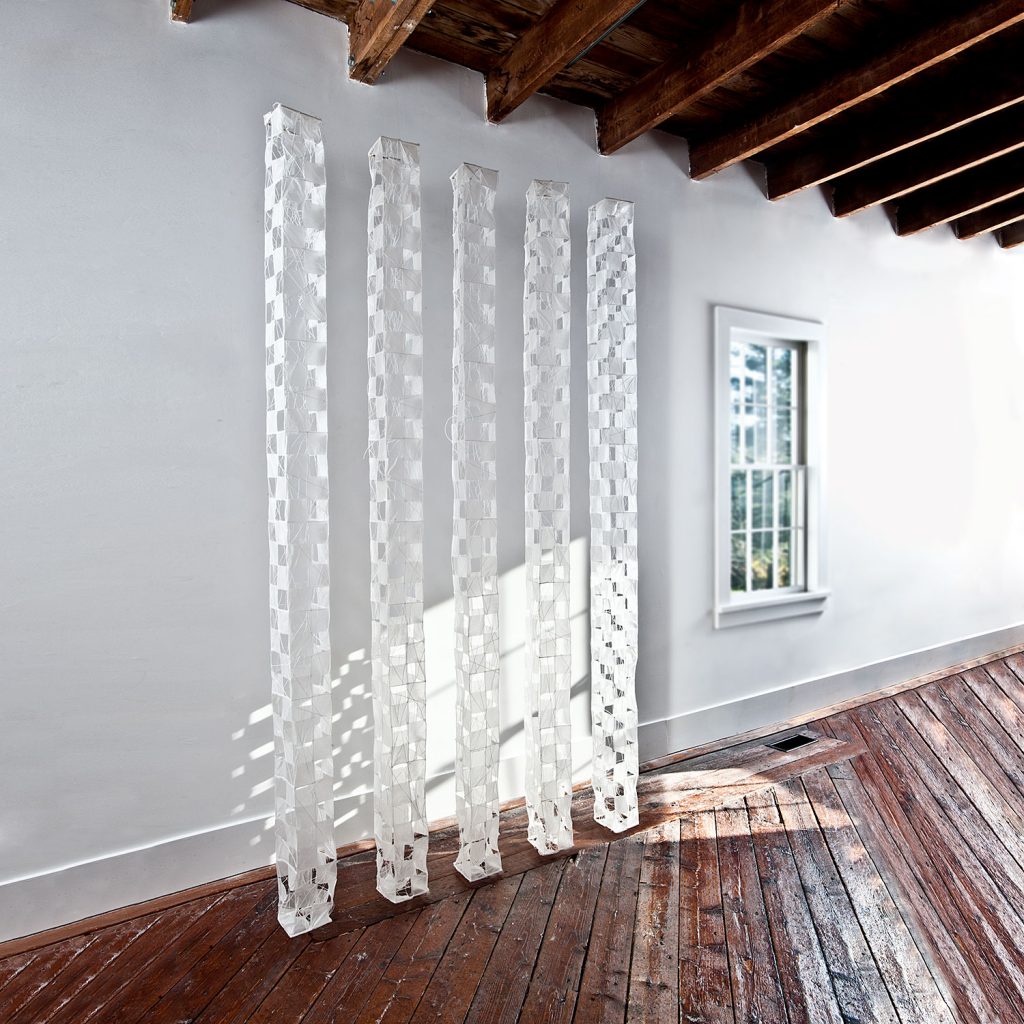
For Paul Furneaux, geographic influences are varied, including time spent in Mexico, at Norwegian fjords and then, Japan, where he studied Japanese woodblock, Mokuhanga “After a workshop in Tokyo,” he writes, “I found myself in a beautful hidden-away park that I had found when I first studied there, soft cherry blossom interspersed with brutal modern architecture. When I returned to Scotland, I had forms made for me in tulip wood that I sealed and painted white. I spaced them on the wall, trying to recapture the moment. The forms say something about the architecture of those buildings but also imbue the soft sensual beauty of the trees, the park, the blossom, the soft evening light touching the sides of the harsh glass and concrete blocks.”