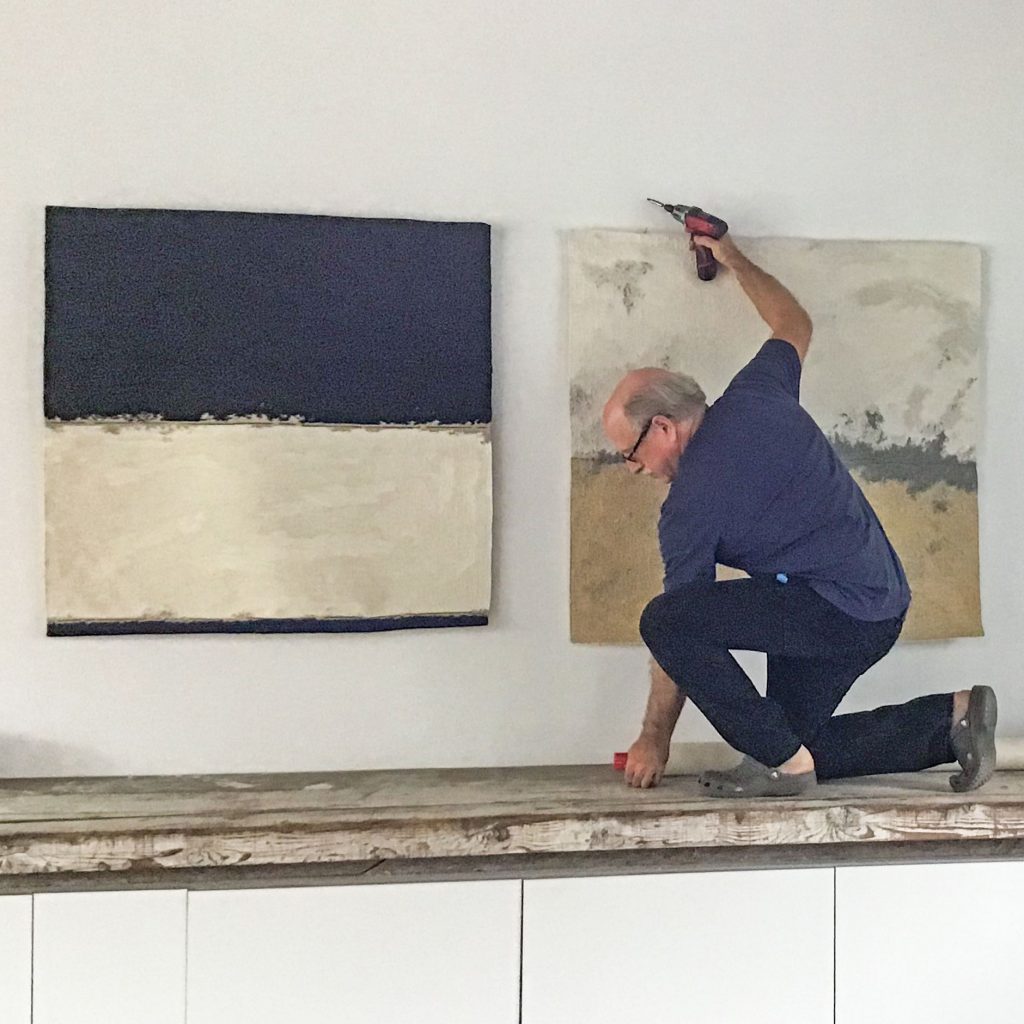
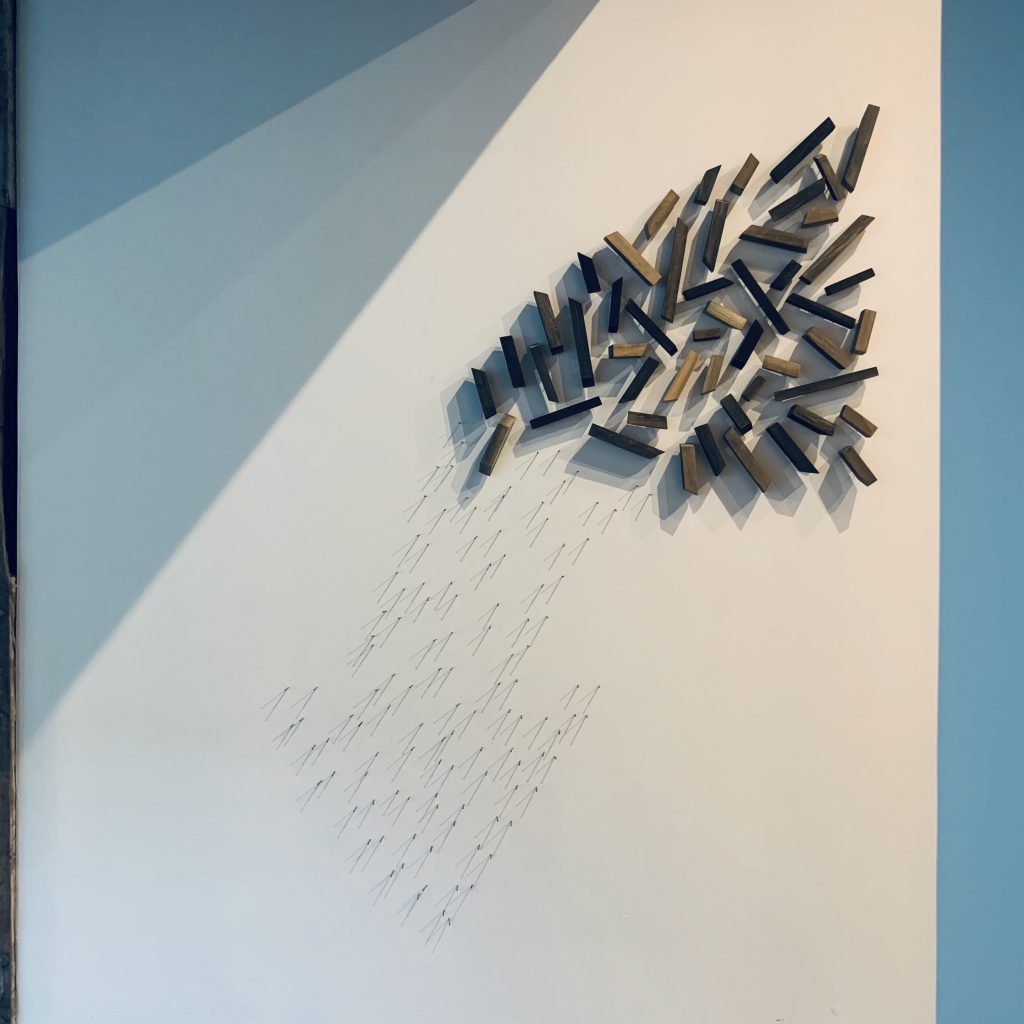
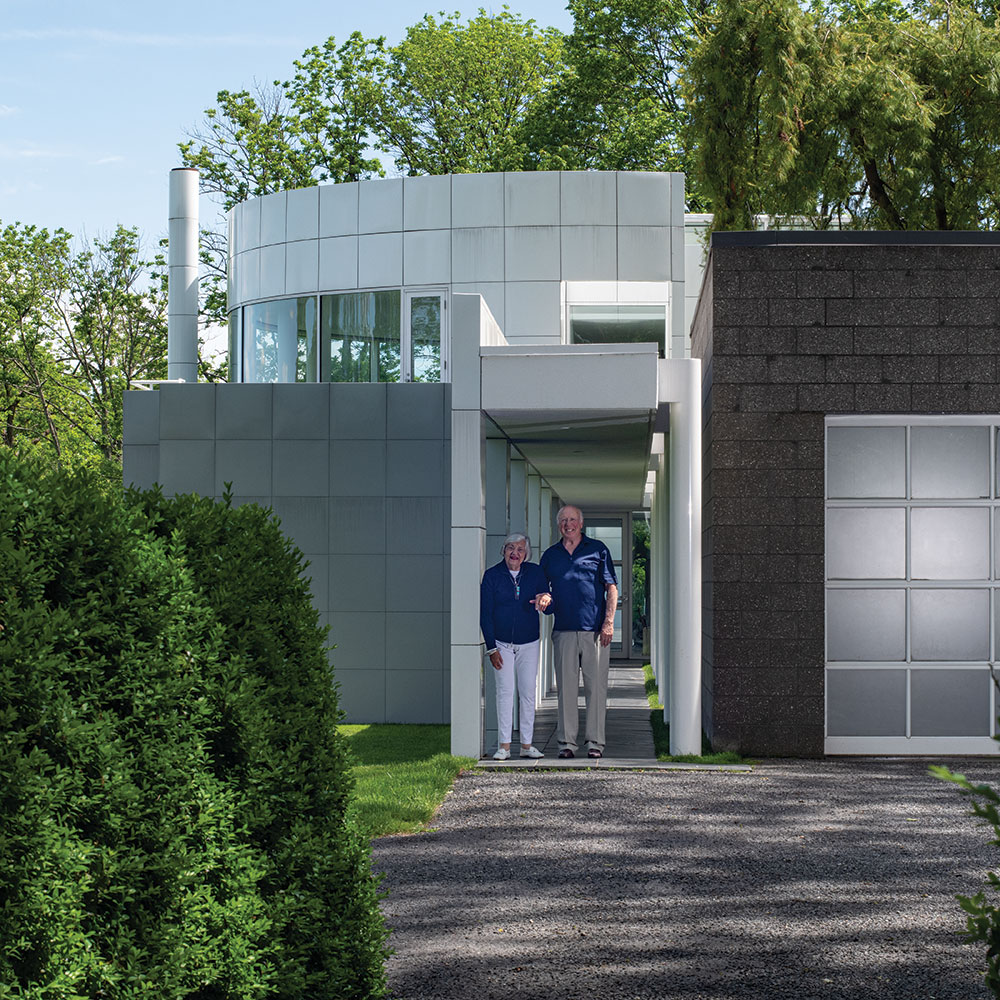
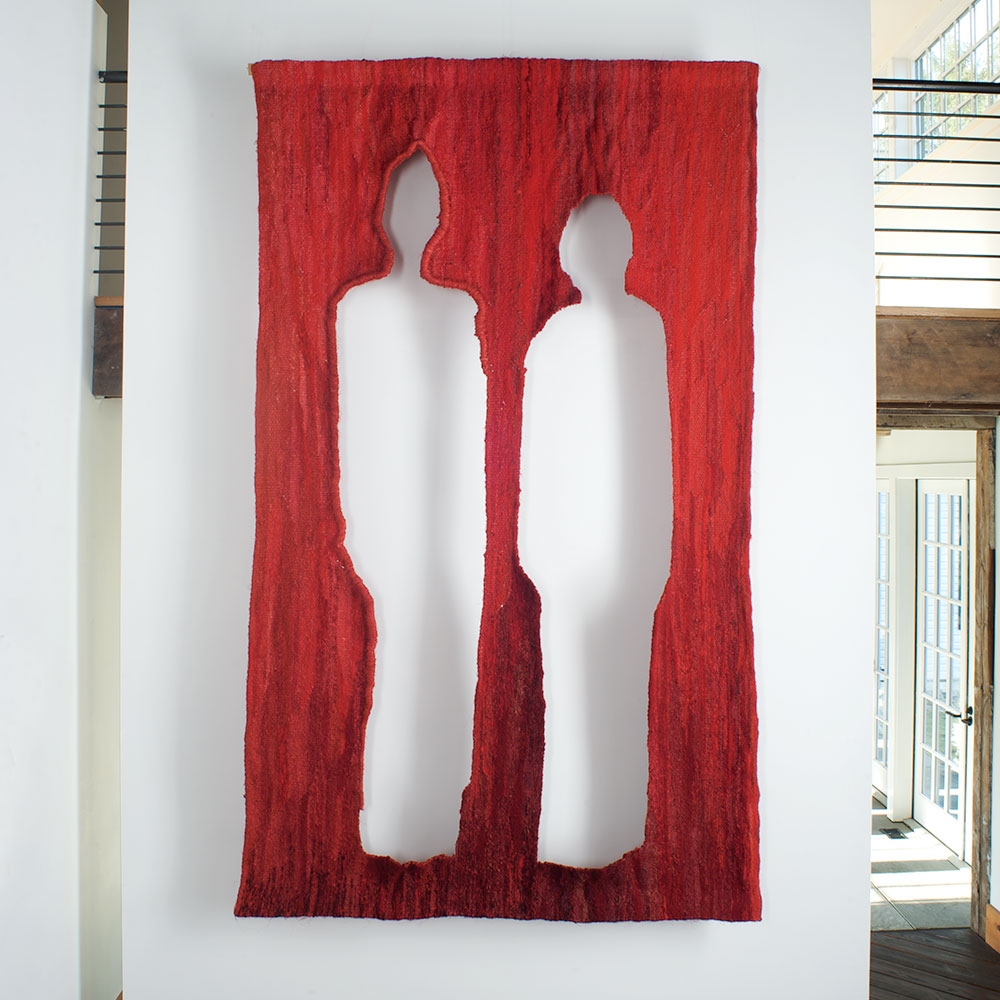
As we kick off Novembers with our release of the Grotta Collection exhibition and book launch, which runs from November 3rd to November 10th, https://www.artsy.net/show/browngrotta-arts-artists-from-the-grotta-collection-exhibition-and-book-launch, we’d like to take a look back on which artist made October so special for us.
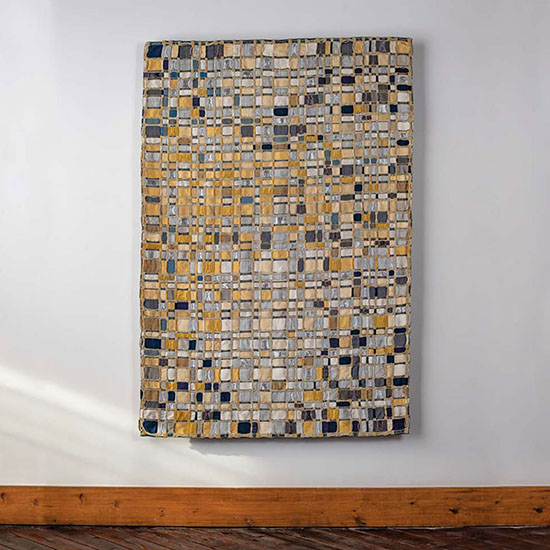

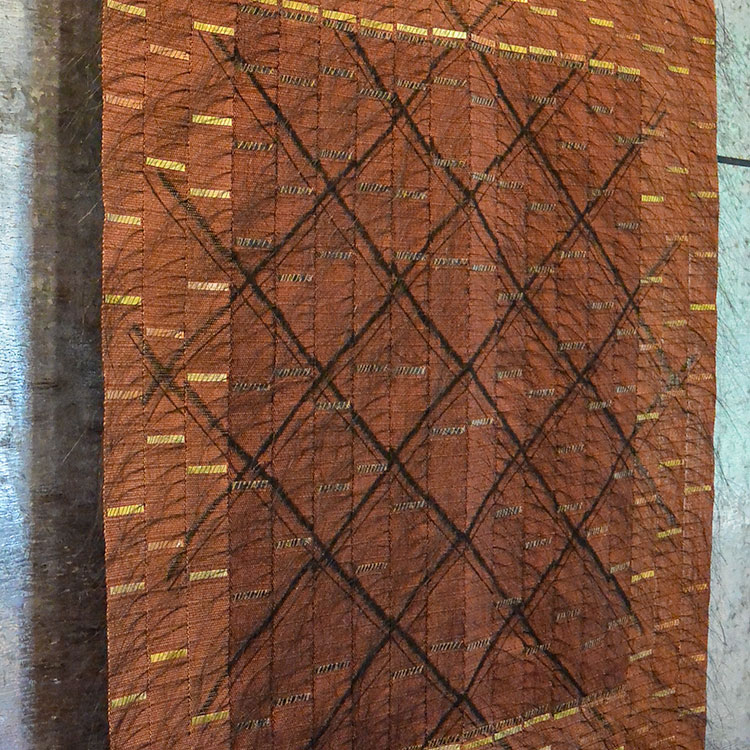
October starts the final quarter of the year, and it also brings in much excitement as the new year is nearing. With new beginnings, we began our New This Week feature in October with works from Eduardo Portillo and Mariá Eugenia Dávila. Their work is driven by their relationship with their surroundings and how their artwork can be communicated within a contemporary textile language. “ We have always been passionate about knowledge, experimentation and especially its reinterpretation within our own place and culture, in Mérida, in the Venezuelan Andes, we also work with local materials, such as cotton and alpaca from Peru and Bolivia, fiber from the moriche and chiqui-chique palm trees of the Orinoco River Delta and Amazon region, as well as dyes from the indigo plant. For us, color is crucial. Our interest in color starts at its very foundations: how it is obtained, where it is found in nature, in objects, in people. Through color, we discover the way to follow each project.” – Eduardo Portillo and Mariá Eugenia Dávila
For more on Eduardo Portillo & Mariá Eugenia Dávila visit Artist Link: http://www.browngrotta.com/Pages/portillo.php

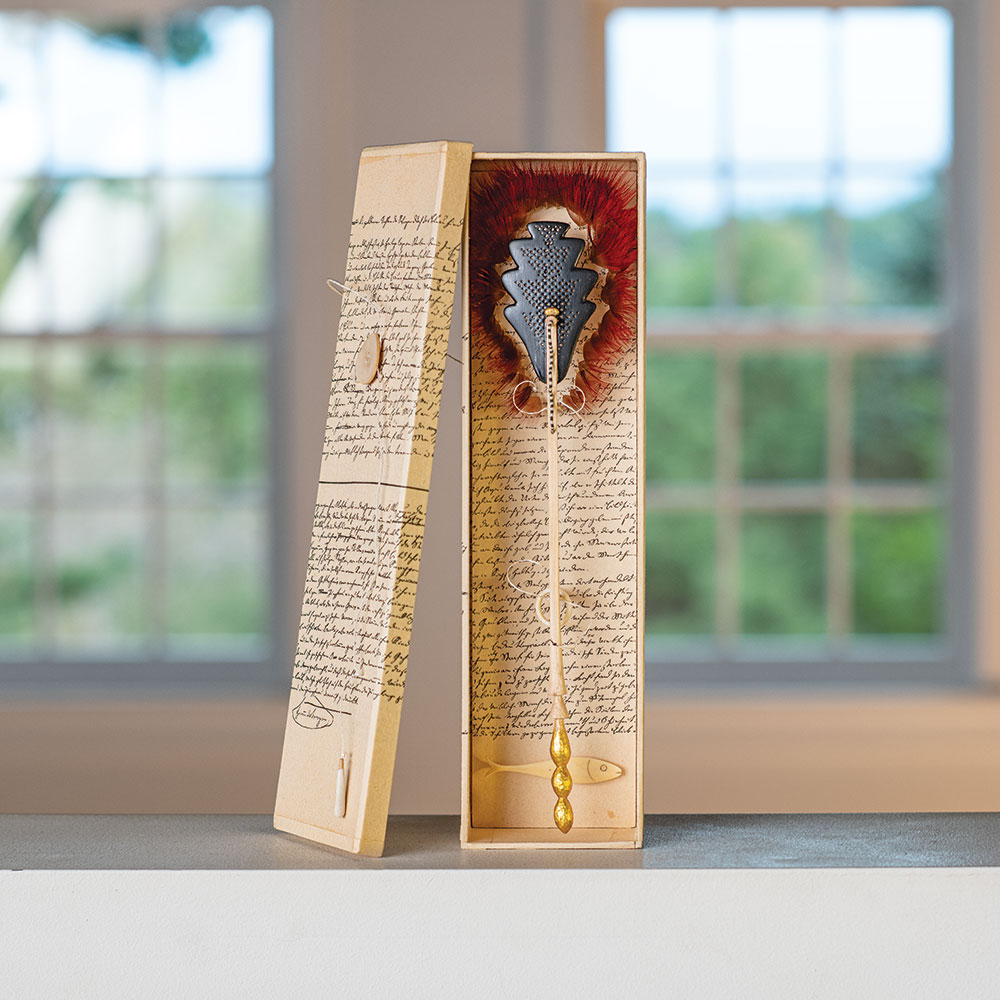
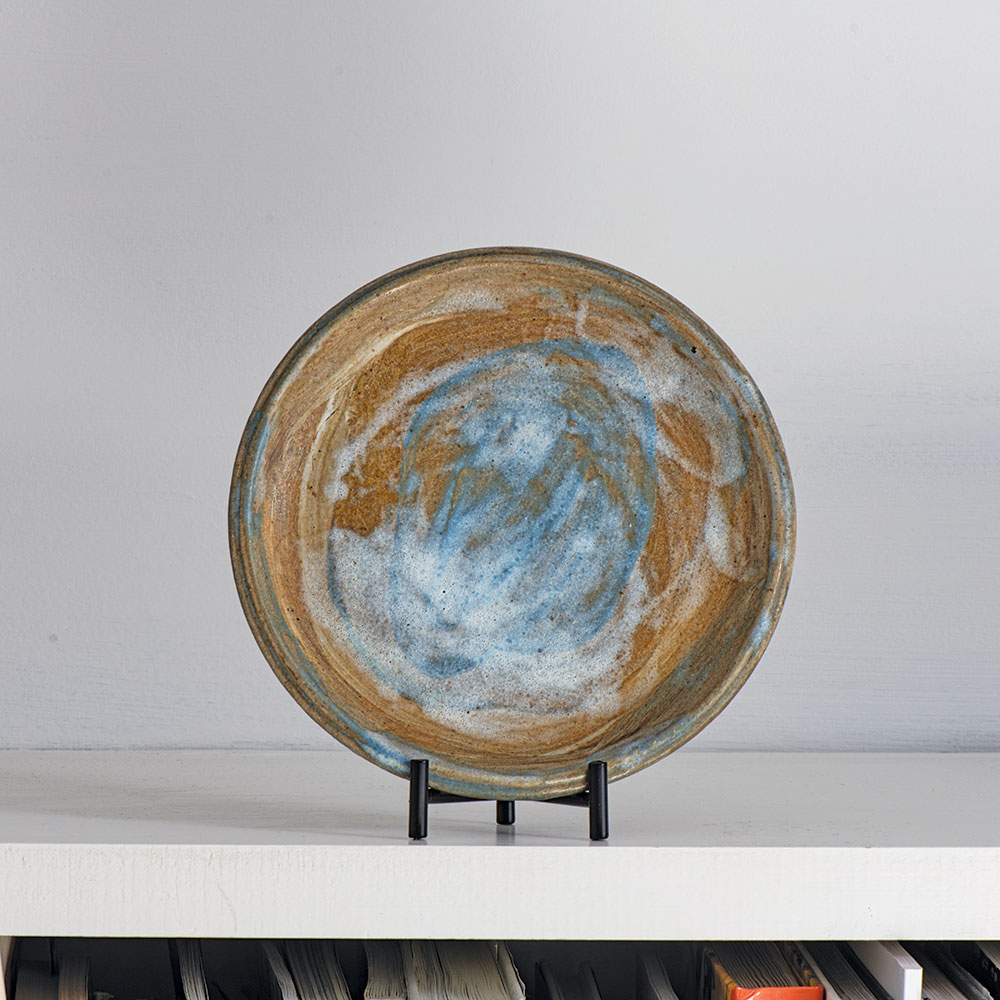
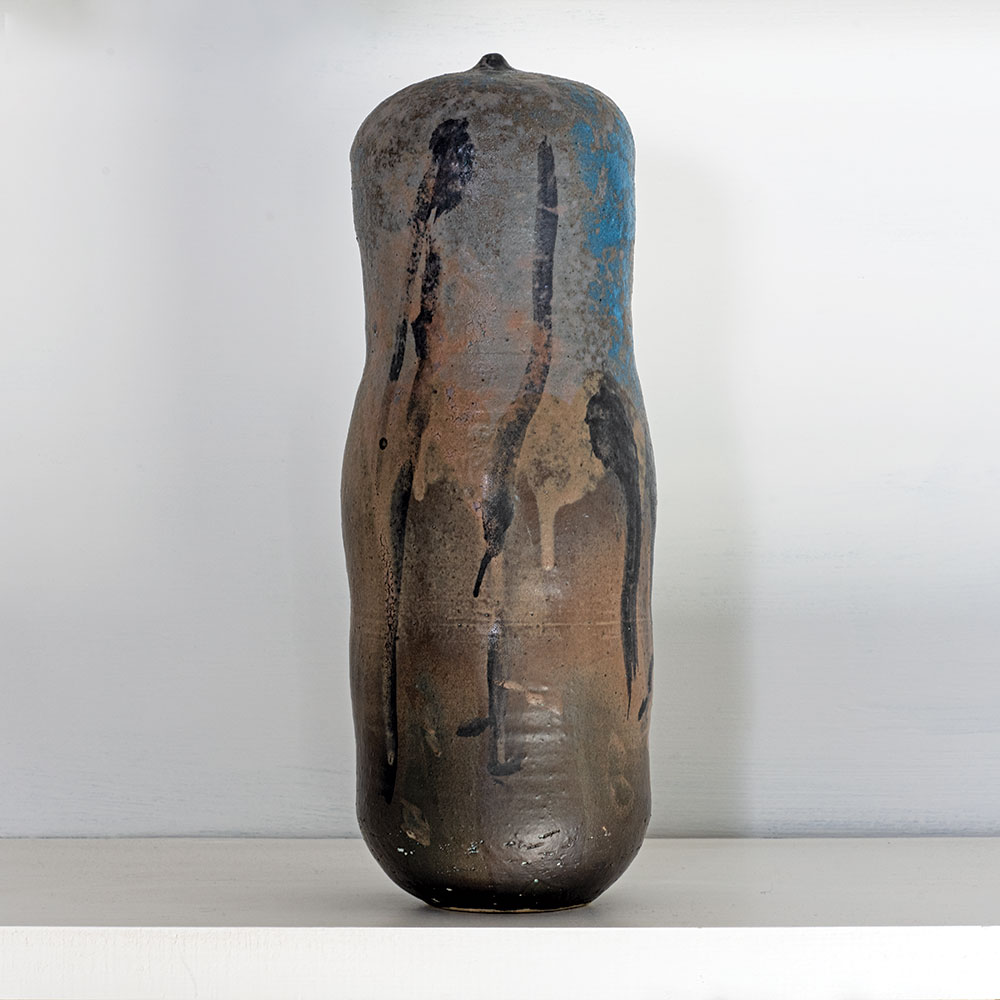
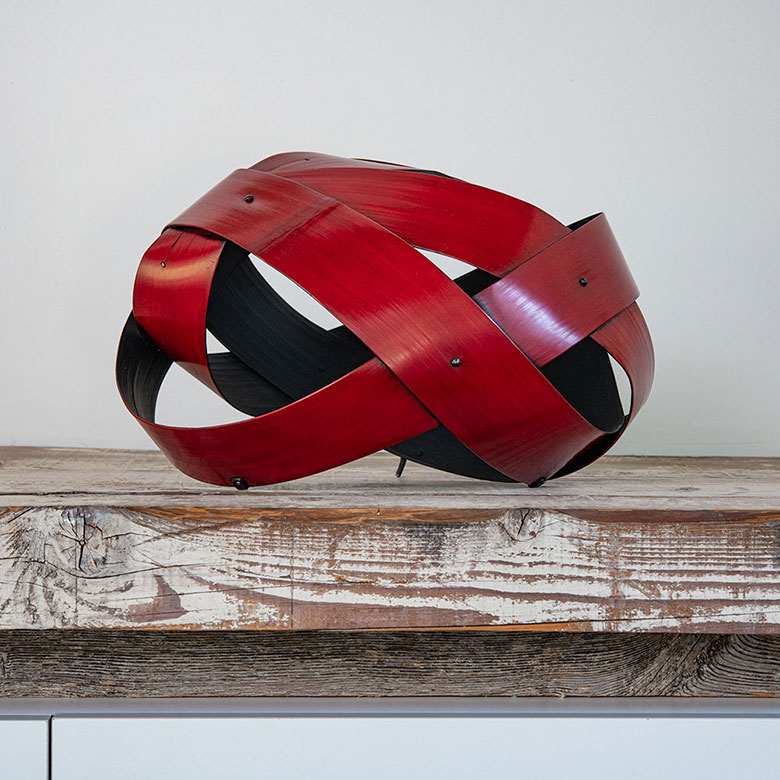
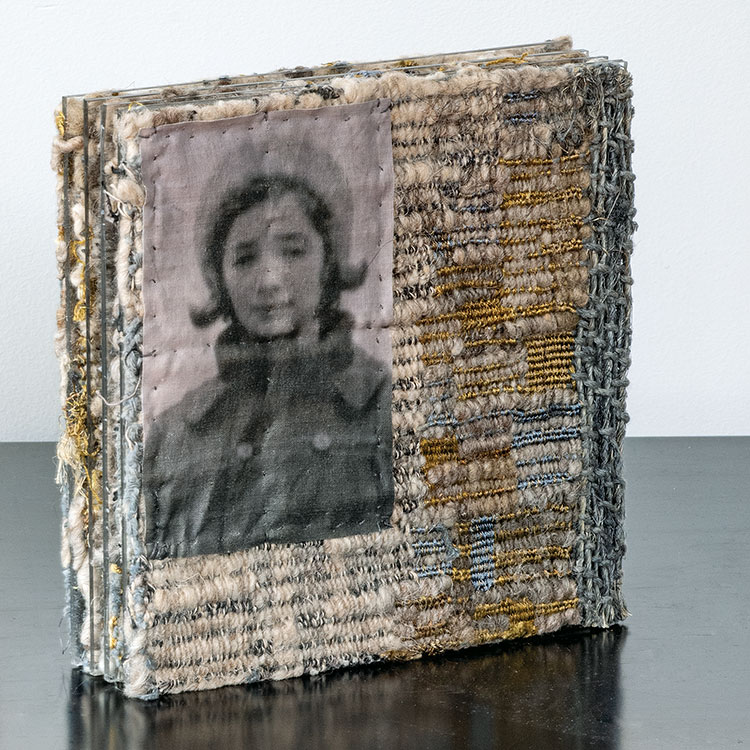
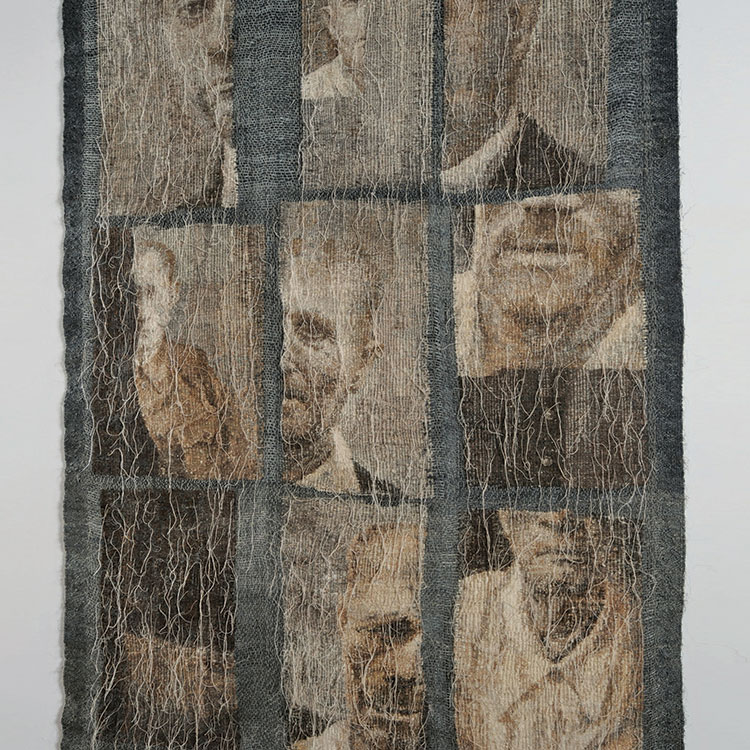
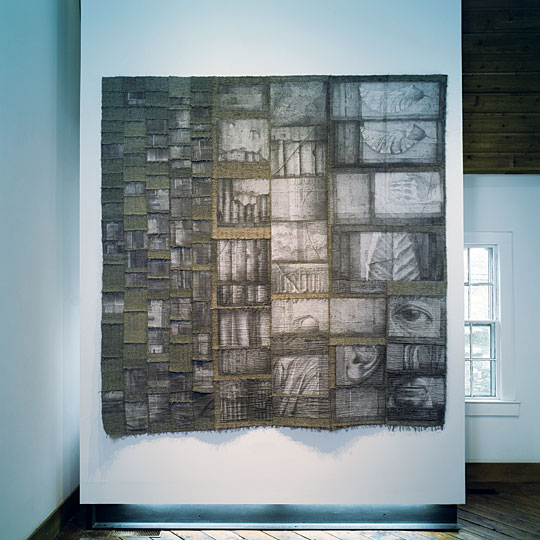
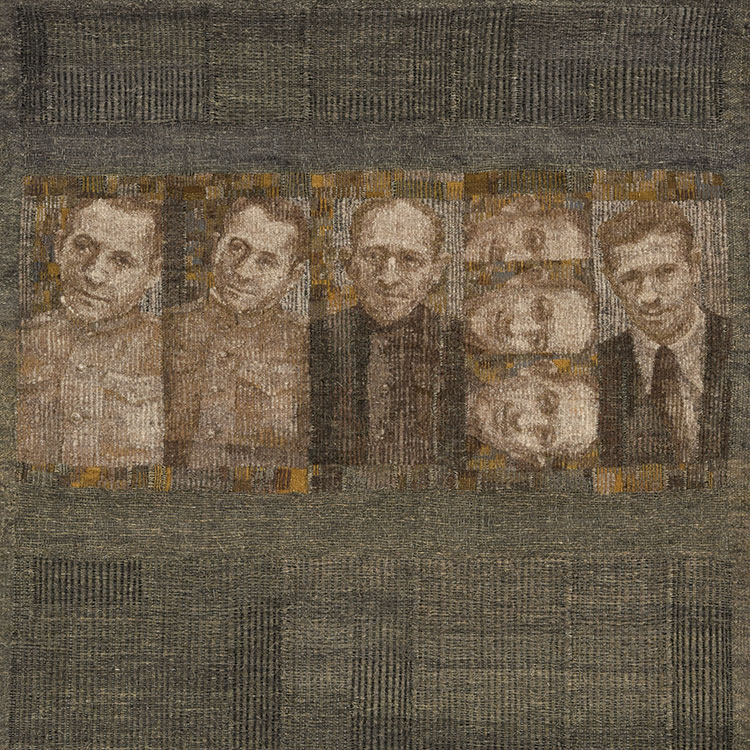
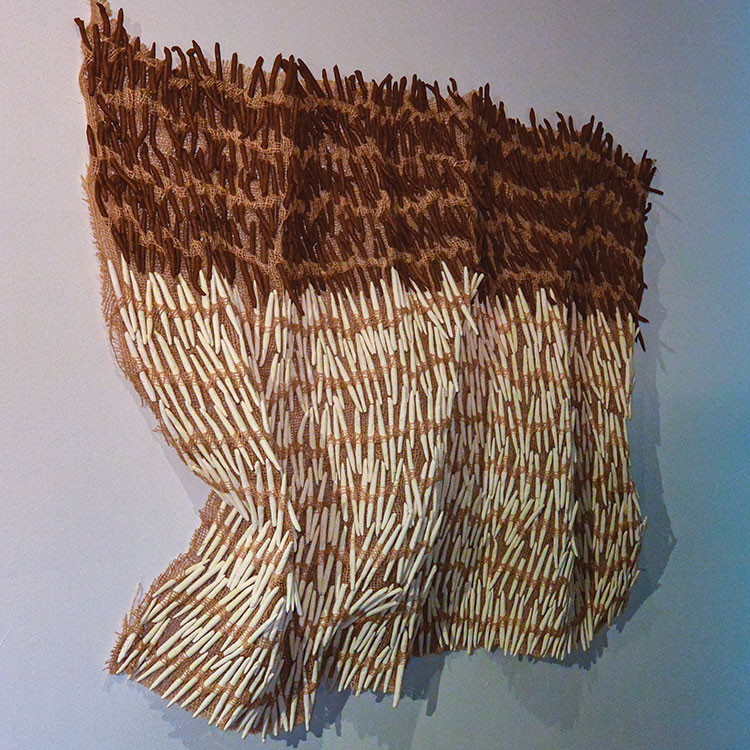
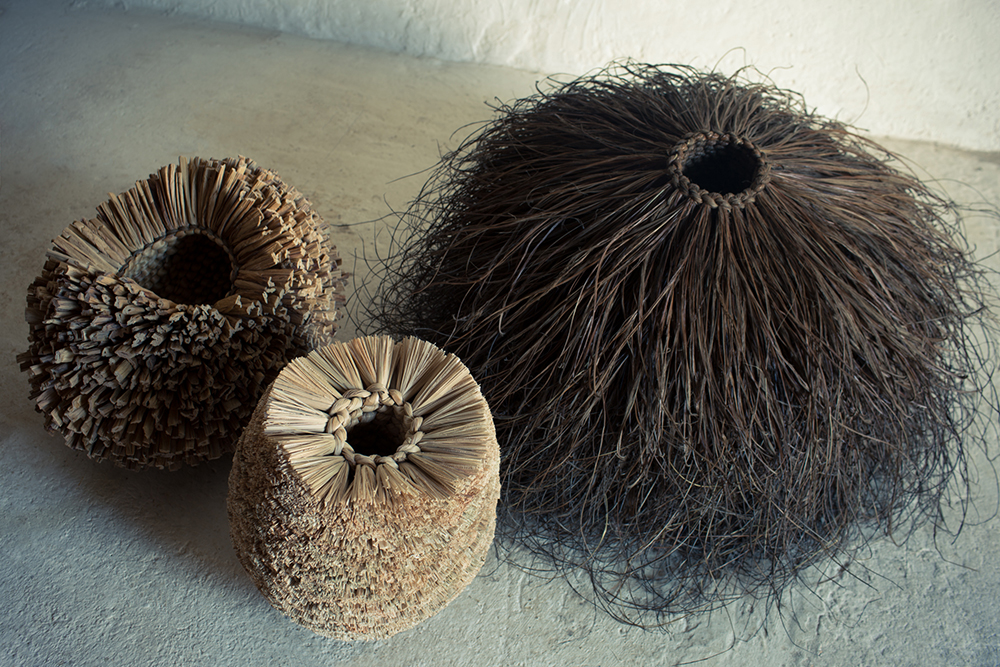
We are always intrigued by the wide variety of artwork that we have the pleasure of showcasing here at browngrotta arts. We strive not only to share the final products but also behind the scenes of the processes that go into creating the work on that ends up on our gallery walls. Our next October New This Week artist was Mary Giles, a St. Croix, Minnesota based fiber artist, and sculptor.
Over the past four decades, Giles helped move the boundaries of basket weaving and earned international recognition for her art, which is characterized by coiled waxed-linen bases adorned with hammered metal or fine wire that brings to mind tree bark, fish scales, feathers or fur.
“My baskets express both action and reaction to what I have loved in the past and what I am discovering today.” Mary Giles
For more on Mary Giles visit Artist Link: http://www.browngrotta.com/Pages/giles.php
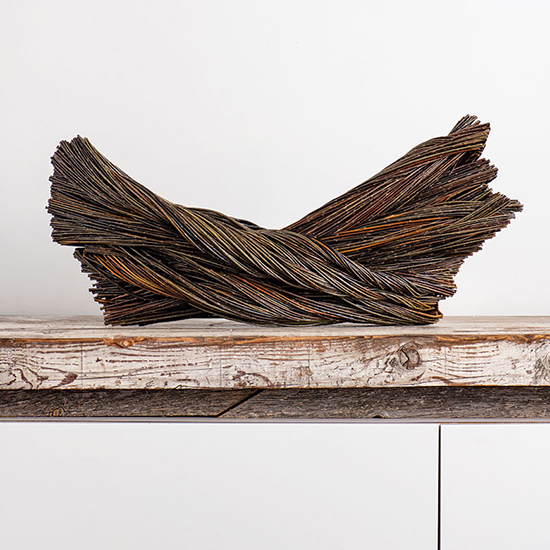

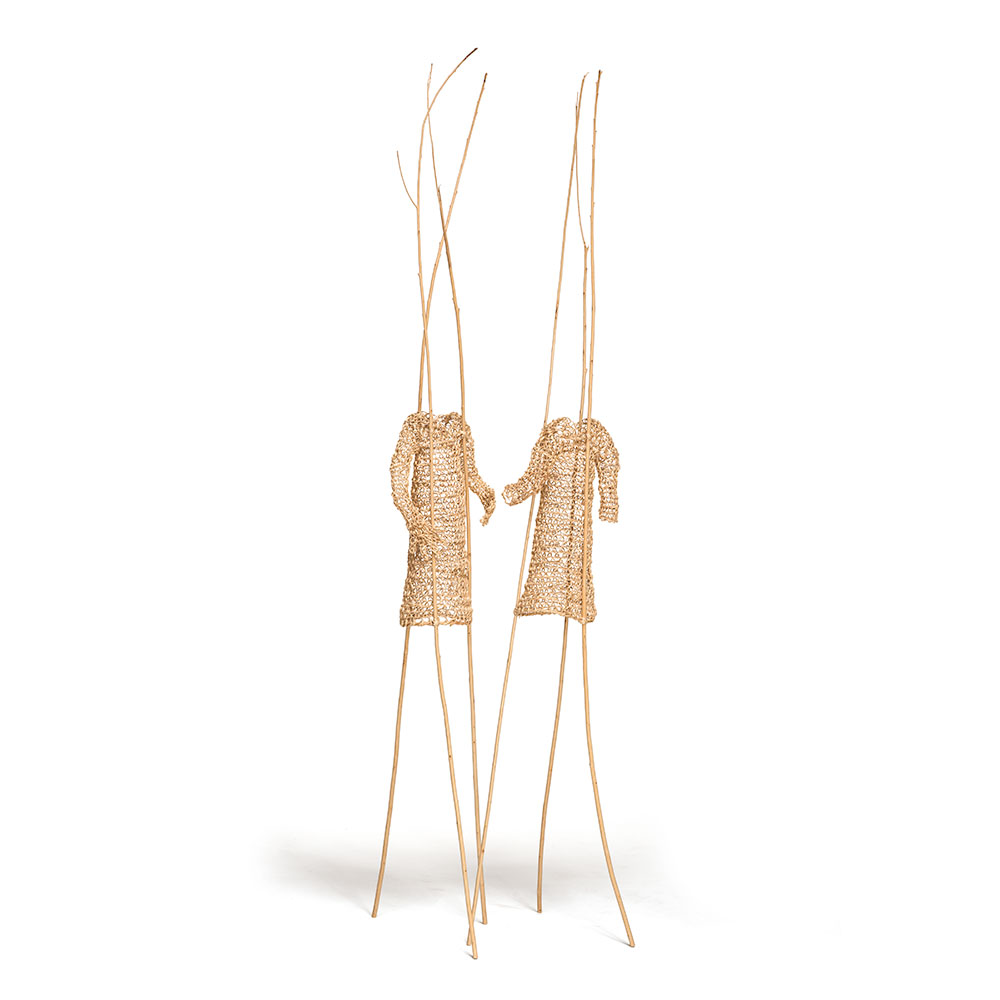
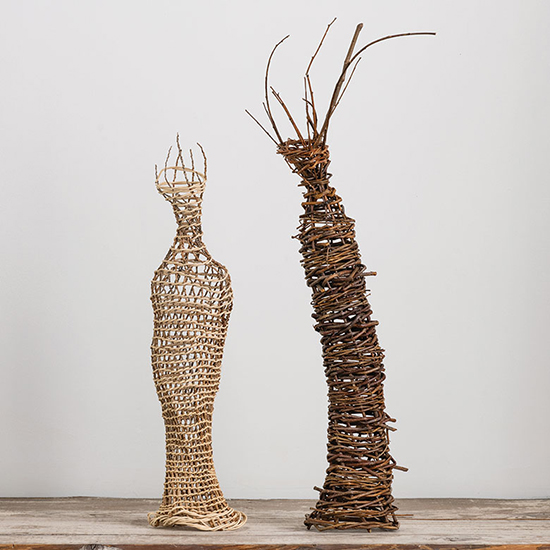
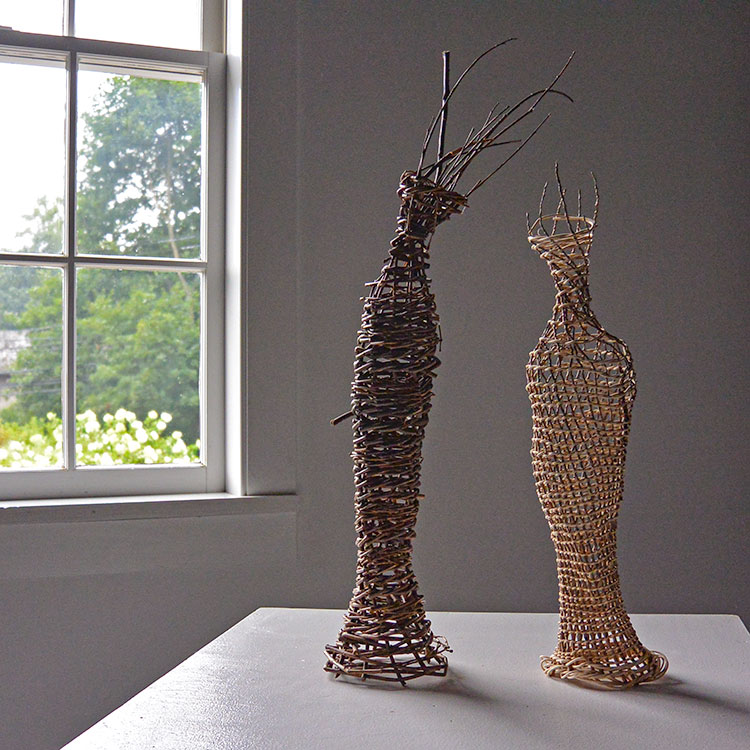
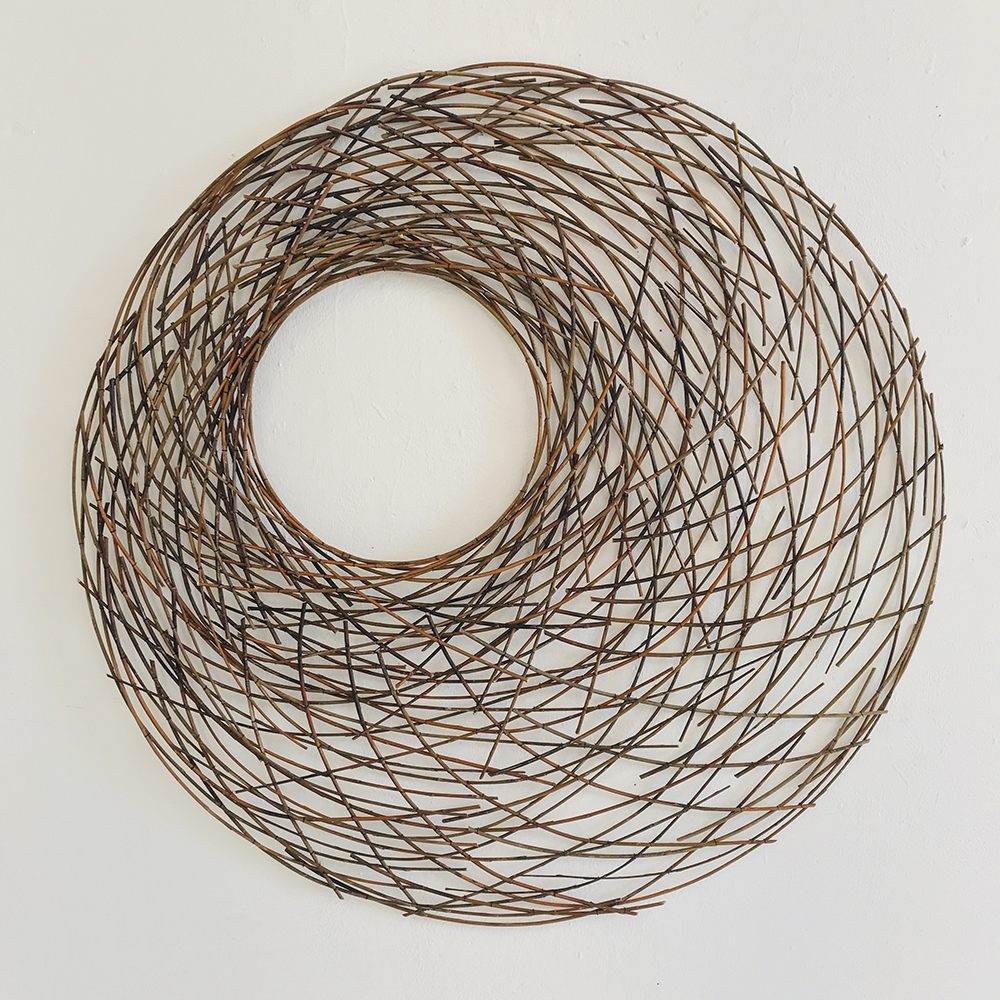
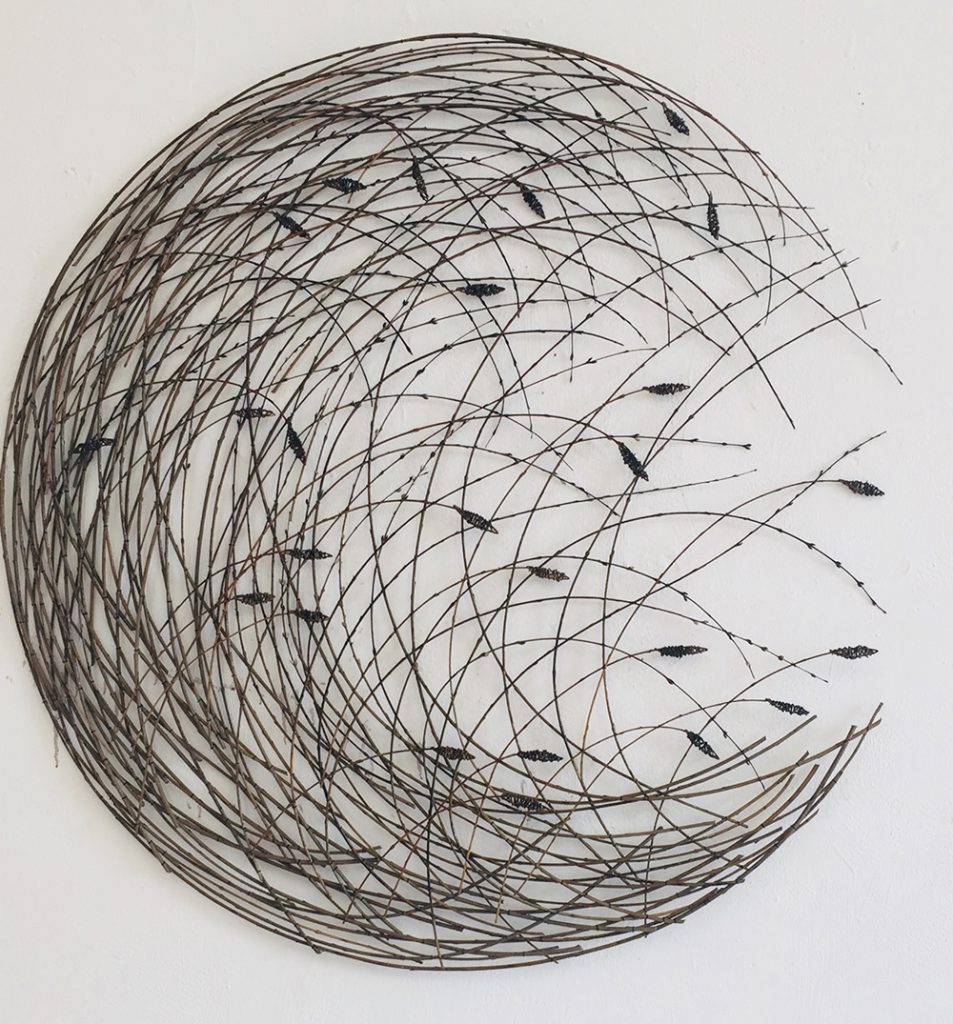
Did you know that Weeping willow trees, which are native to northern China, are beautiful and fascinating trees whose lush, curved form is instantly recognizable? Did you also know that in addition to her basketmaking addiction, Christine Joy is also addicted to the smell of willow branches. In her studio, you will find willow branches that are piled high, and even when she doesn’t have time to make something, she takes a little visit into her very own willow heaven as much as she can. “Because it takes so long for one work of art, it has really become my own art therapy, which is ironic because that is what I got my degree in, to help others through art,” Joy said. “But now making these expressions is my. Willow is my life.”
For more on Christine Joy visit Artist Link: http://www.browngrotta.com/Pages/joy.php
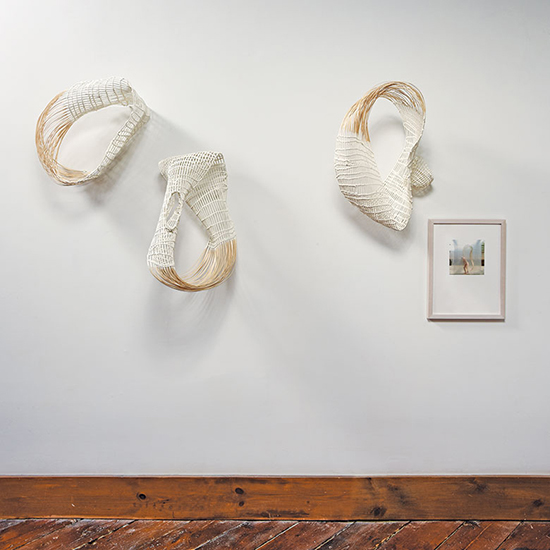

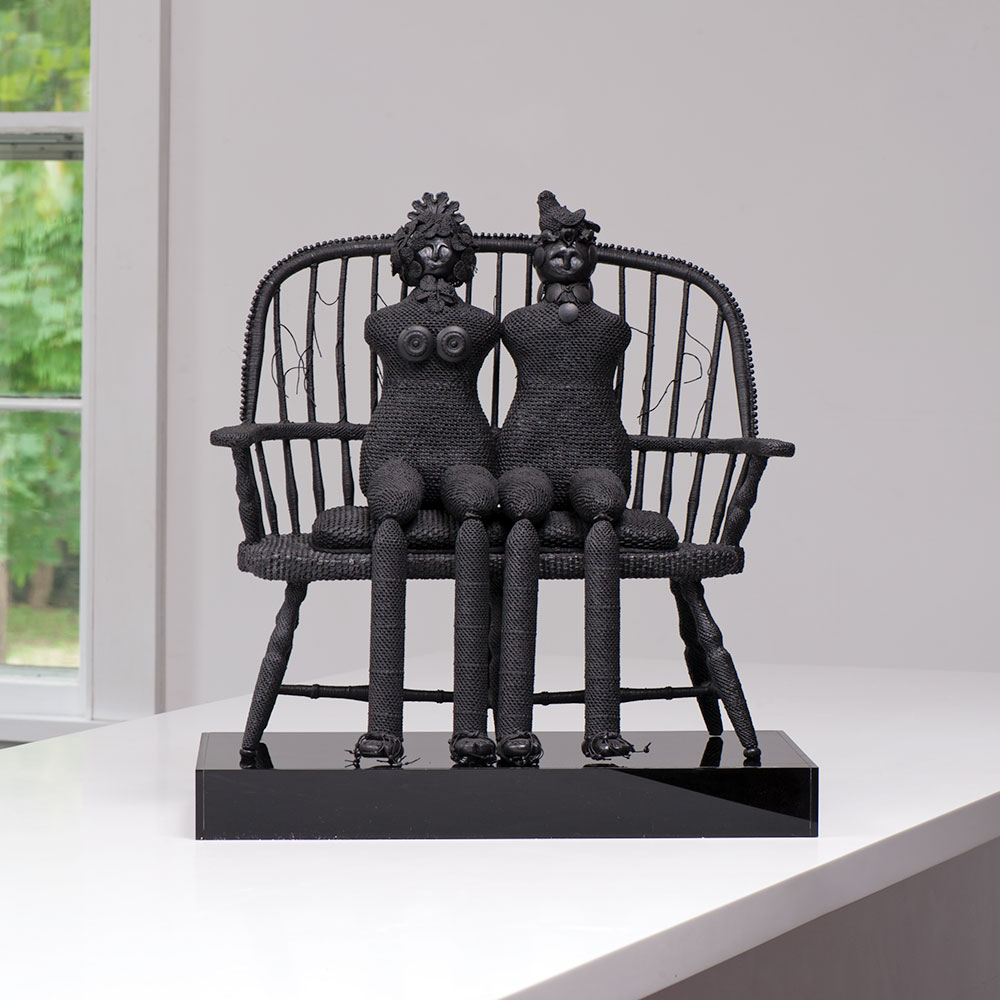
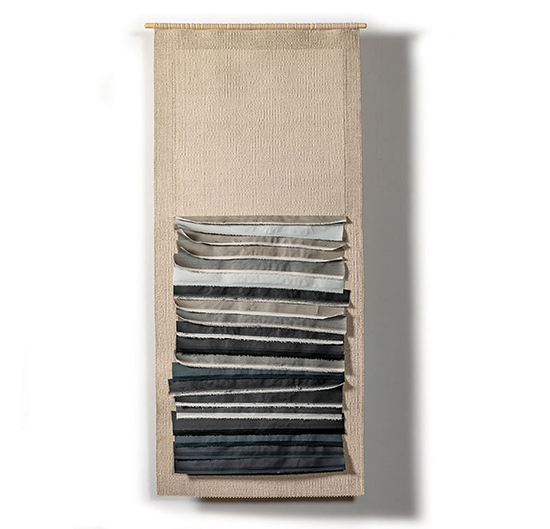
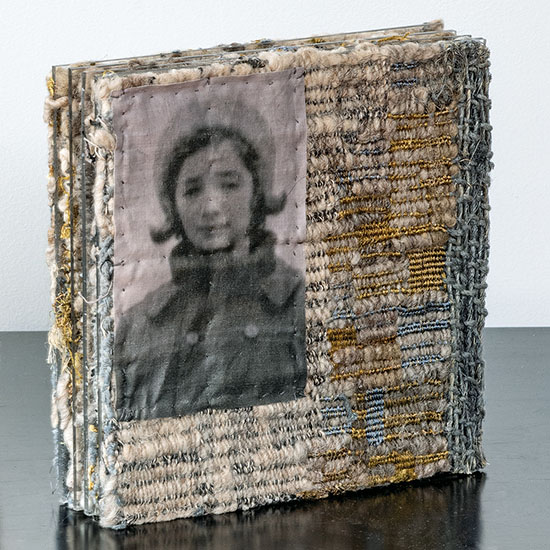
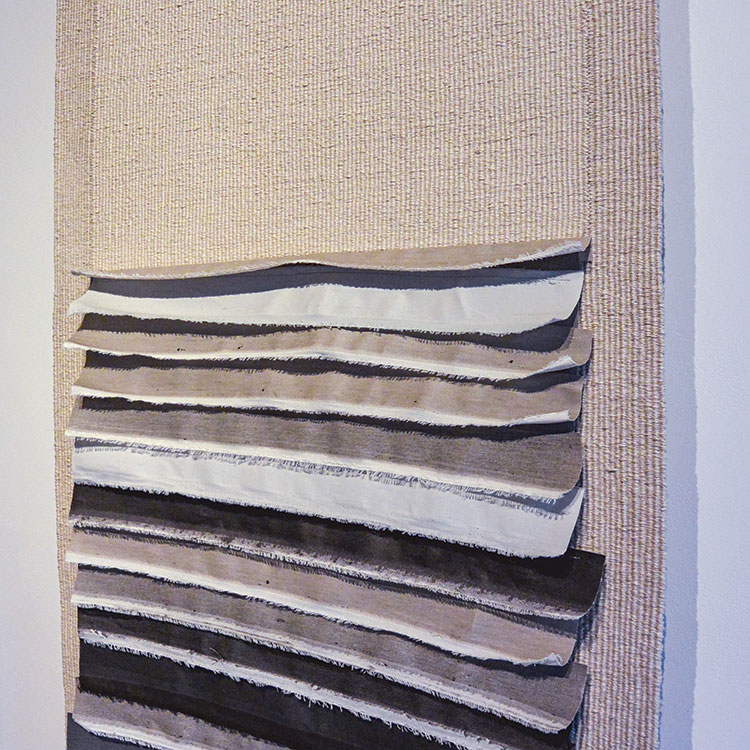
One of the great joys we have is having the opportunity to share such fantastic work with incredible artists from all over the world. It is a pleasure sharing works from Stéphanie Jacques from Belgium in our new book The Grotta Home by Richard Meier: A Marriage of Architecture and Craft. Stéphanie Jacques once said, “Connecting things is the foundation of my work: hard and soft, old and new, valuable and trivial, conscious and unconscious, human and plant.”
For more on Stéphanie Jacques visit: http://www.browngrotta.com/Pages/jacques.php