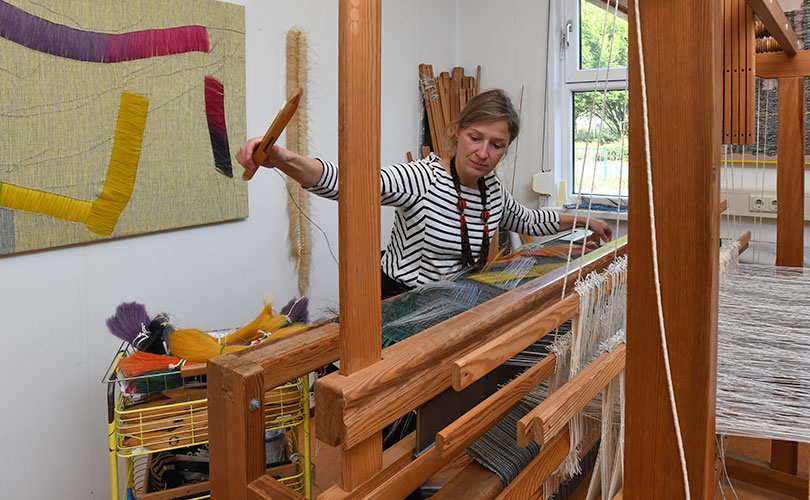
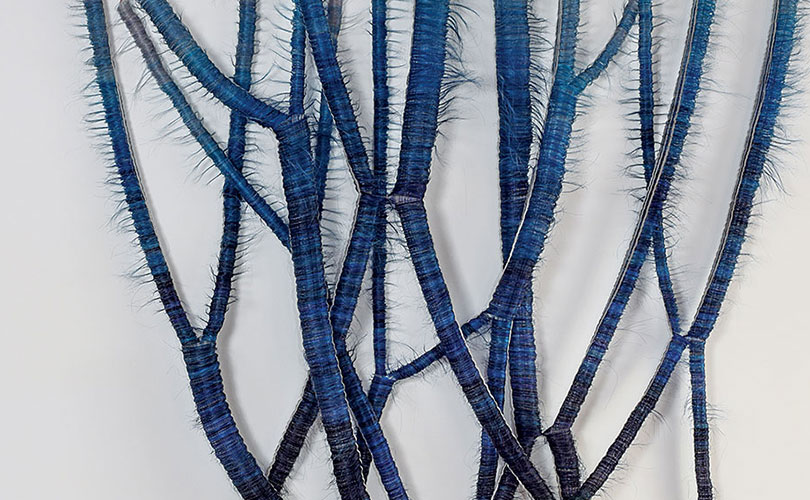
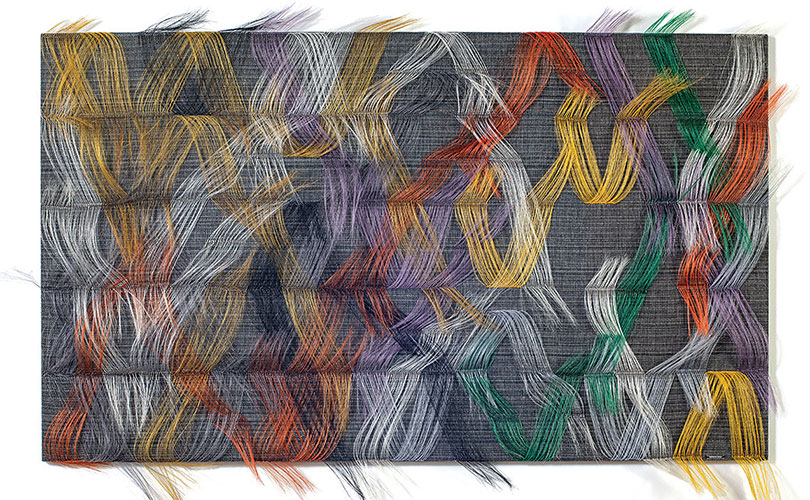
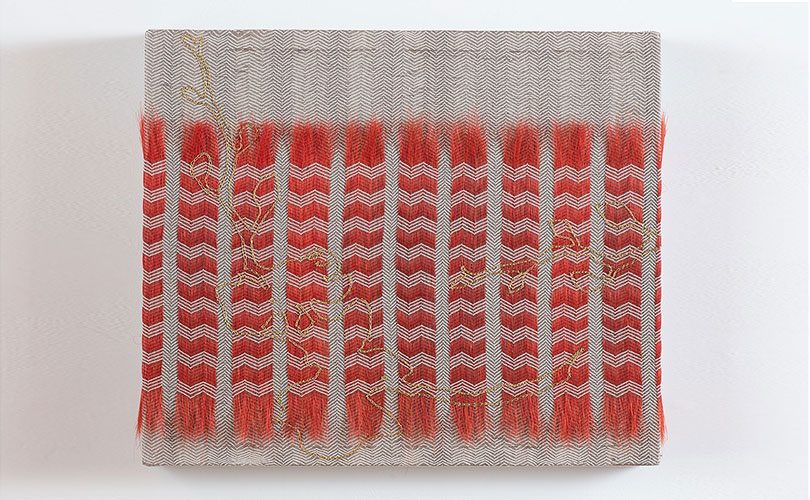
As we wrote earlier this month, in December 2021, we were asked to talk to a group of fiber artists about trends we had observed in browngrotta arts’ 30+ years in the art textiles field. Here is second of two arttextstyle posts on the insights we shared with that group. In the last post (January 12, 2022) we spoke about fiber art’s resurgence from 2004 on, after a few decades of the medium’s being on the art world’s out list. In this post, we’ll discuss two art trends that we have seen propel fiber art’s growing popularity.
Democratization
The most important of these trends is the democratization of the art experience which the internet, among other cultural changes, has wrought. Art lovers now find work by scrolling the internet from the Google home page to museums’ digitized collections. Pinterest users compile images of artwork they find everywhere. Art lovers do not approach art chronologically as museums required or by movement or medium or by fine art versus decorative art. Galleries and museums are no longer the gatekeepers. Current art viewers have no patience for exclusionary labels – they are content to just like what they like. In a corresponding change, online sales have quadrupled in the last several years, doubling between 2019 to 2020 alone.
Galleries and Museums Take Note
The move toward a more inclusive approach to art and artists is evident in what galleries exhibit. It wasn’t that many years ago that an art fair we attended posted large signs dividing Fine Art from the section that housed glass, ceramics and other mediums, Our booth was near the signs and we saw people abruptly turn heel, rather than look at artwork labeled other than “fine art.” Quite a contrast to today’s Art Basel booths, where a mix of media – often including fiber art – is the norm.

Museums have been forced to respond to democratization, too. Fiber art is not the only medium that has benefited from this trend – all craft media have. The Ceramic Presence in Modern Art at the Yale Art Gallery in 2015, masterfully combined 80 ceramics with paintings from their permanent collection by artists such as de Kooning, Noguchi and Mark Rothko. The curators cited a dissolution of boundaries and hierarchies, where artists bear less allegiance to any particular historical medium or tradition, opting instead to use “whatever materials best suit their ideas at a given moment.”

The trend toward democratization means a pointed inclusion of women artists and artists from underrepresented groups. Traditionally excluded by curators and critics, institutions have committed to changing the racial and gender composition of their collections. The reopening of MoMA in 2019, announced, with great fanfare, “a reimagined approach to its presentation of modern and contemporary art.” A work by newly appreciated Indian fiber artist Meernalini Mukherjee held center court. CBS News reported that MoMA planned to add five times as many women artists as before to its collection. And Director Glenn Lowry described the elimination of departments and the creation of displays that would mix paintings, sculpture, photography, architecture, design and new media in a way that feels much more “whole and real.”
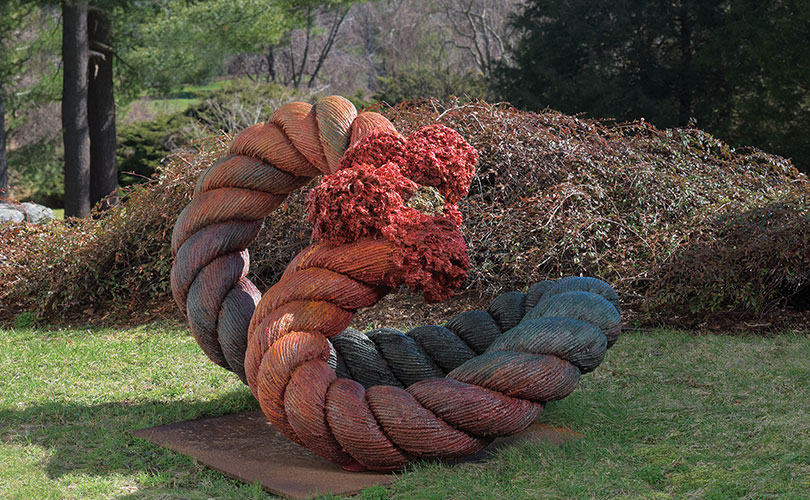

Appreciating Art Without Labels
We’ve seen this new openness to art – without labels — in our business, too. Fewer people compare work we show to other art forms – no longer needing to place it in a context that’s familiar. We’ve sold important work through online platforms to clients that we have next-to-no contact with, including a large tapestry to an executive in Peru and the 300-pound sculpture pictured in this post to a large company in Indonesia. And museums are willing to look at art that’s by artists other than the stalwarts of the field. We’ve placed work by Eduardo Portillo and Mariá Dávila, Venezuela, Aleksandra Stoyanov of Israel and Chang Yeonsoon of Korea in museum collections. As Forbes Magazine notes: “The expectation that craft techniques will be seen in an art museum … allows the techniques to flourish, to facilitate new artistic expression, and to make new meaning.”
Democratization (and the pandemic) has meant that people are more willing to find art in unexpected places – including a renovated barn in Wilton, Connecticut. We’ve had busloads of students from Canada, textile fans from Chile, collectors from California, and curators from Illinois, Minnesota and Missouri. More people now travel to us from New York and fewer people balk at buying art from Connecticut and not New York.
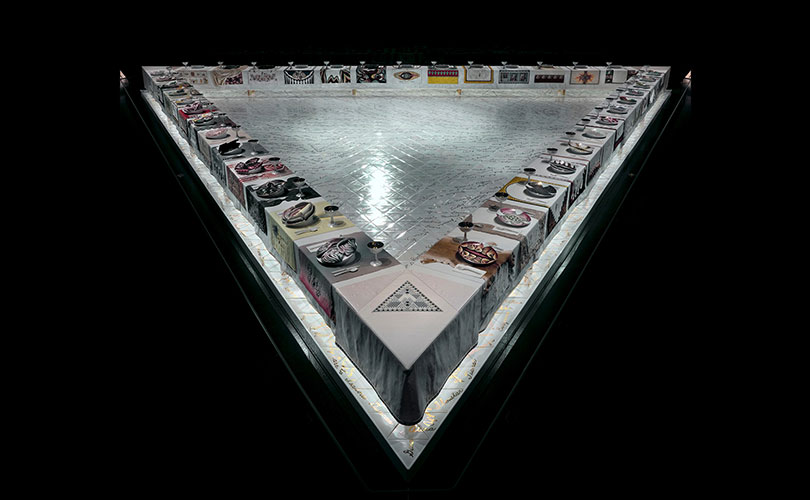

Illustrating concerns about political issues and the environment
A second trend we’ve observed in the last decade is a more explicit presentation of concerns about political issues and the environment. The re-examination of the origins of fiber in the last few years brought attention to the important role that feminism had played, particularly in the 70s – as artists used fiber art to take a provocative stance against the male domination of “pure” art forms such as Minimalism. Judy Chicago’s The Dinner Party is probably the best-known feminist work from this period; it was the subject of a retrospective at the de Young Museum in San Francisco last December. Chicago and other artists of the period like Miriam Shapiro and Faith Ringgold consciously sought to reclaim those mediums, traditionally considered “craft,” as fine art mediums, equivalent to painting and sculpture.
In the last decade, craft techniques, those identified as women’s work in particular, have again been reappropriated by emerging artists as ways to address feminist and other current issues. The NYT realized in 2018 that “Some of the Most Provocative Political Art is Made With Fibers,” observing that “… a generation later, fiber art looks fresh again.” With threads and hair, fabric and flags, Sonya Clark examines the African experience and the harmful legacy of the Confederacy. Artists Sophie Narrett and Orly Cogan use embroidery to highlight what Narrett calls “the freedoms and restraints of femininity.” Bisa Butler has reinvented quilting – a traditionally marginalized medium—to explore the historical marginalization of her subjects.
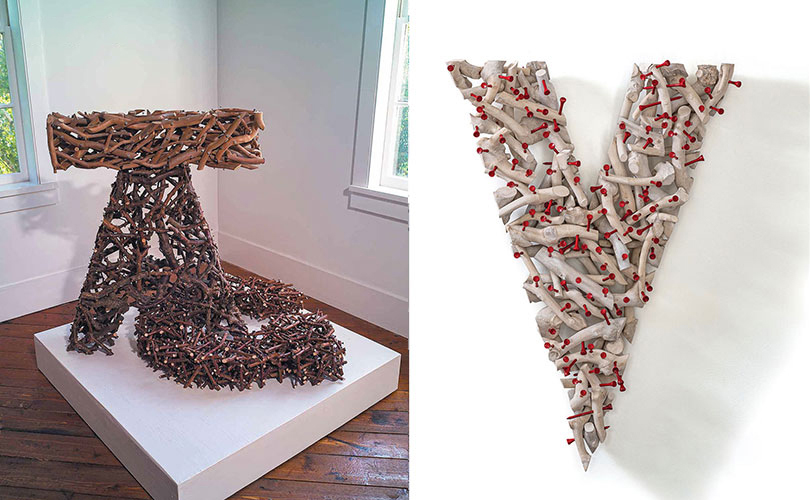

At browngrotta arts, one of the artists we represent, Gyöngy Laky, who studied fiber at Berkeley in the 70s, has always reflected her activism In her work. Slowly (2002) can spell “LAG” or “GAL.” It makes a statement on the lack of female faculty in the University of California system. On the right is Variant, a newer work, made of painted branches and red golf tees, that makes a statement about the coronavirus and Trump’s inattention.
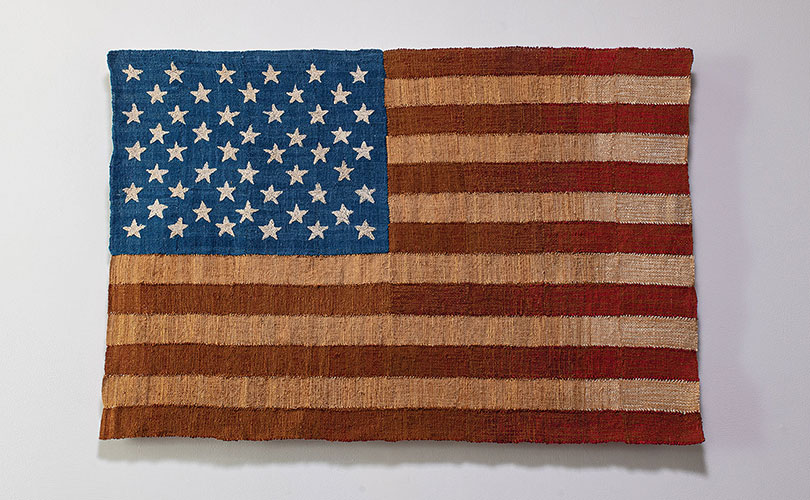

James Bassler has spent a lifetime investigating Peruvian and cube weaving and other techniques and materials like nettle and cochuyi. In some of his works, though, the political takes center stage. An earlier flag was meant to be hung upside down as a statement on current events. A flag he made last year is entitled They’re Ready for Their Seat at the Table. “The recent street action of all these young people has really inspired me,” he wrote us. “For years I’ve held on to some wonderful handspun cotton from Guatemala, dark, dark brown and some lighter natural brown hand spun from Oaxaca. Well the dark brown has become the warp to replace the red and the brown cotton replaces the white. There will be a trace of red amongst the dark brown, I don’t want to completely wipe out the Puritans,” he says. ”I just want room for everyone to sit at the table.”
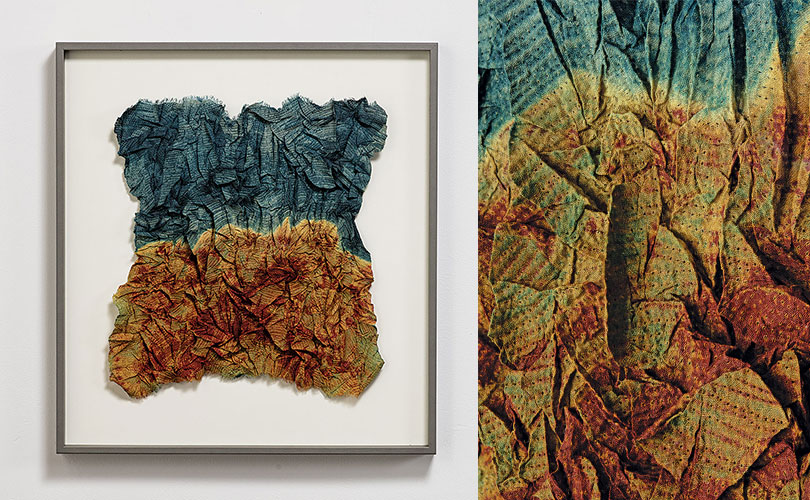

Neha Puri Dhir from India says she is generally inclined to look inwards for inspiration which brings a sense of peace and empathy to her work. “But gradually, the growing disquiet around me became impossible to ignore,” she says describing has work Forest Fire. “Polluted water table, climate change, extinction of species, and forest fires – made me anxious. The complexity of these layered thoughts, could no longer be expressed in closed geometric shapes. Art adapted itself to the chaos within…,” she says.
As we concluded in Trends Observed, Part 1, it’s an exciting time to work with fiber artist and to promote art textiles and fiber sculpture. Thanks for joining browngrotta on this journey.