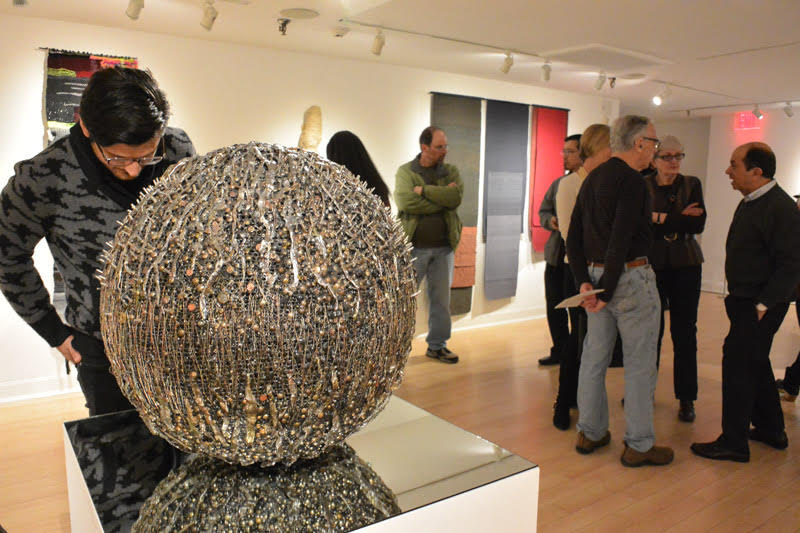
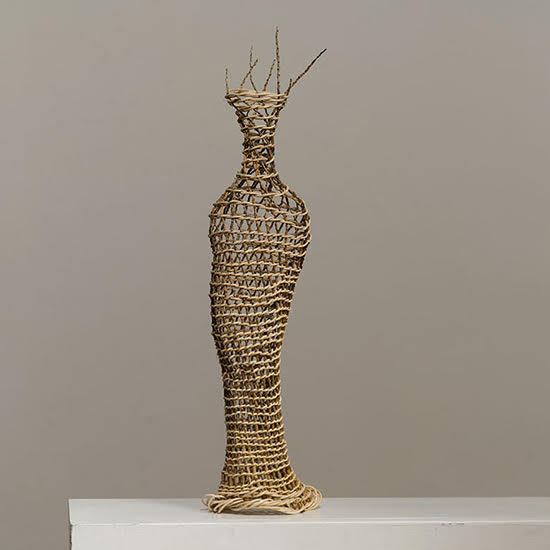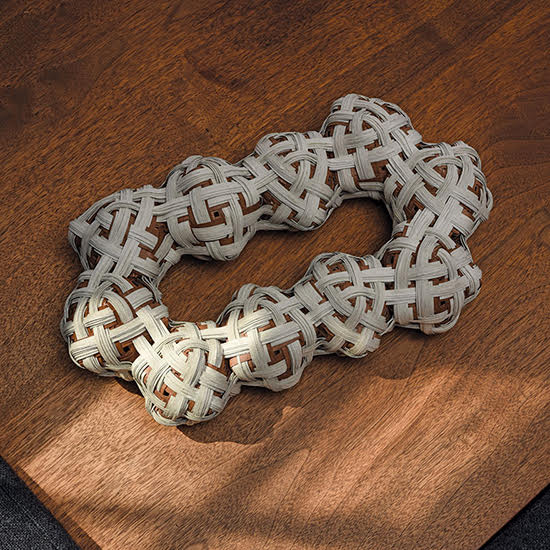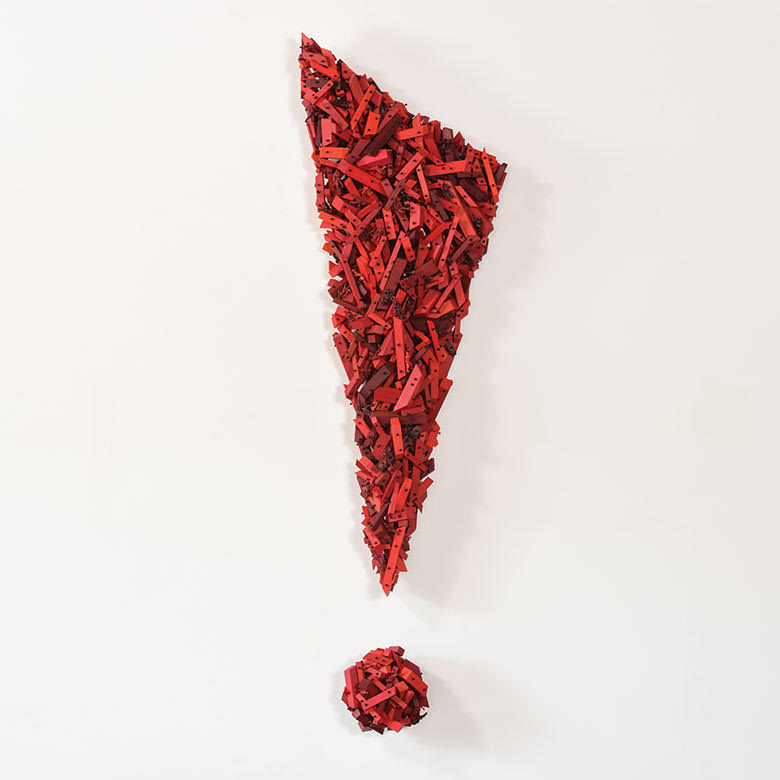
Norma Minkowitz’s Excavation in the foreground, Carolina Yrarrázaval’s tapestries in the background.
Last Friday, the Westport Arts Center opened up its new exhibition, Handmade: Women Reshaping Contemporary Art, which includes three artists, Chiyoko Tanaka, Carolina Yrarrázaval and Norma Minkowitz, represented by browngrotta arts. The exhibition was curated by Elizabeth Gorayeb, the Executive Director of the Wildenstein Plattner Institute, Inc., a New York based non-profit committed to art historical research. Handmade also features work by Ghada Amer, Anna Betbeze, Ligia Bouton, Orly Cogan, Lesley Dill, Terri Friedman, Sermin Kardestuncer, Sophia Narrett, Faith Ringgold, Miriam Schapiro, Judith Scott, Beverly Semmes, Rosemarie Trockel and Margo Wolowiec, all of whom utilize fiber and textile in their art.
301 balls (Diptych), 2017
Cotton thread, coal from Soma, Turkey, fabric
36 × 37 in, 2017. Photo by Tom Grotta
“As visitors to a gallery or museum, we are expected to engage with works of art though the act of looking. We consider the final product of the artist’s creation, but rarely do we think of the tactile experience of the artist’s process,” explains Gorayeb. “Fiber art — works of art created from wool, silk, cotton, flax and other forms of textiles — present us with a dynamic, multi-sensory experience.” It is because of this tactile experience and physical commitment that Narrett prefers embroidery over painting, “when an object is developed by human hands for hundreds of hours, it leaves a quality in the surface that can be sensed,” she notes.













